Ultrasound-Triggered Effects of the Microbubbles Coupled to GDNF Plasmid-Loaded PEGylated Liposomes in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 29686604
- PMCID: PMC5900787
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00222
Ultrasound-Triggered Effects of the Microbubbles Coupled to GDNF Plasmid-Loaded PEGylated Liposomes in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
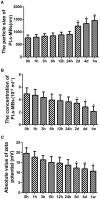
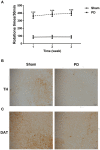
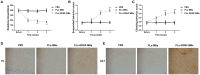
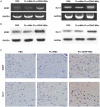
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate ultrasound-triggered effects of PEGylated liposomes-coupled microbubbles mediated gene transfer of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) plasmid (PLs-GDNF-MBs) on behavioral deficits and neuron loss in a rat model of Parkinson's disease (PD). Methods: The unloaded PLs-MBs were characterized for particle size, concentration and zeta potential. PD rat model was established by a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesion. Rotational, climbing pole, and suspension tests were used to evaluate behavioral deficits. The immunohistochemical staining of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine transporter (DAT) was used to assess the neuron loss. The expression levels of GDNF and nuclear receptor-related factor 1 (Nurr1) were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR analysis. Results: The particle size of PLs-MBs was gradually increased, while the concentration and absolute zeta potential were gradually decreased in a time-dependent manner after injection. 6-OHDA elevated amphetamine-induced rotations and decreased the TH and DAT immunoreactivity compared to sham group. However, these effects were blocked by the PLs-GDNF-MBs. In addition, the mRNA and protein expression levels of GDNF and Nurr1 were increased after PLs-GDNF-MBs treatment. Conclusions: The delivery of PLs-GDNF-MBs into the brains using MRI-guided focused ultrasound alleviates the behavioral deficits and neuron loss in the rat model of PD.
Keywords: GDNF; PEGylated liposomes; Parkinson's disease; microbubbles; ultrasound.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-triggered effects of the microbubbles coupled to GDNF- and Nurr1-loaded PEGylated liposomes in a rat model of Parkinson's disease.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jun;119(6):4581-4591. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26608. Epub 2018 Mar 7. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29240240
-
Non-invasive, neuron-specific gene therapy by focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening in Parkinson's disease mouse model.J Control Release. 2016 Aug 10;235:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.05.052. Epub 2016 May 26. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27235980
-
Ultrasound-responsive neurotrophic factor-loaded microbubble- liposome complex: Preclinical investigation for Parkinson's disease treatment.J Control Release. 2020 May 10;321:519-528. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.044. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32112852
-
Adenoviral vector-mediated delivery of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor provides neuroprotection in the aged parkinsonian rat.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001 Nov;28(11):896-900. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03544.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11703392 Review.
-
Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Delivery in Parkinson's Disease: A Delicate Balance between Neuroprotection, Trophic Effects, and Unwanted Compensatory Mechanisms.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Apr 10;11:29. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00029. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 28442998 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GDNF improves the cognitive ability of PD mice by promoting glycosylation and membrane distribution of DAT.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 1;14(1):17845. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68609-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39090173 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Research on Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Opening for Neurological Disorders: A Review.Neurol Int. 2023 Feb 14;15(1):285-300. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15010018. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 36810473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles for drug delivery in Parkinson's disease.J Neurol. 2021 May;268(5):1981-1994. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10291-x. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33141248 Review.
-
Mechanistic Insight from Preclinical Models of Parkinson's Disease Could Help Redirect Clinical Trial Efforts in GDNF Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11702. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111702. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Therapy: The Next-Generation Therapeutics and Their Delivery Approaches for Neurological Disorders.Front Genome Ed. 2022 Jun 22;4:899209. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2022.899209. eCollection 2022. Front Genome Ed. 2022. PMID: 35832929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apuschkin M., Stilling S., Rahbek-Clemmensen T., Sørensen G., Fortin G., Herborg Hansen F., et al. . (2015). A novel dopamine transporter transgenic mouse line for identification and purification of midbrain dopaminergic neurons reveals midbrain heterogeneity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 42, 2438–2454. 10.1111/ejn.13046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

