CALHM3 Is Essential for Rapid Ion Channel-Mediated Purinergic Neurotransmission of GPCR-Mediated Tastes
- PMID: 29681531
- PMCID: PMC5934295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.043
CALHM3 Is Essential for Rapid Ion Channel-Mediated Purinergic Neurotransmission of GPCR-Mediated Tastes
Abstract
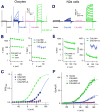
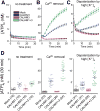
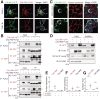
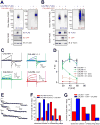
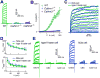
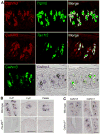
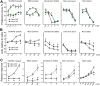
Binding of sweet, umami, and bitter tastants to G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in apical membranes of type II taste bud cells (TBCs) triggers action potentials that activate a voltage-gated nonselective ion channel to release ATP to gustatory nerves mediating taste perception. Although calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is necessary for ATP release, the molecular identification of the channel complex that provides the conductive ATP-release mechanism suitable for action potential-dependent neurotransmission remains to be determined. Here we show that CALHM3 interacts with CALHM1 as a pore-forming subunit in a CALHM1/CALHM3 hexameric channel, endowing it with fast voltage-activated gating identical to that of the ATP-release channel in vivo. Calhm3 is co-expressed with Calhm1 exclusively in type II TBCs, and its genetic deletion abolishes taste-evoked ATP release from taste buds and GPCR-mediated taste perception. Thus, CALHM3, together with CALHM1, is essential to form the fast voltage-gated ATP-release channel in type II TBCs required for GPCR-mediated tastes.
Keywords: ATP release; blue-native page; concatemer; hexamer; knockout; mouse; patch-clamp electrophysiology; single-molecule photobleaching; taste bud; voltage-gated.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
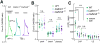
Comment in
-
Opening a "Wide" Window onto Taste Signal Transmission.Neuron. 2018 May 2;98(3):456-458. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.04.020. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 29723496 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes.Nature. 2013 Mar 14;495(7440):223-6. doi: 10.1038/nature11906. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23467090 Free PMC article.
-
How do taste cells lacking synapses mediate neurotransmission? CALHM1, a voltage-gated ATP channel.Bioessays. 2013 Dec;35(12):1111-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300077. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 24105910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Action potentials and ion conductances in wild-type and CALHM1-knockout type II taste cells.J Neurophysiol. 2017 May 1;117(5):1865-1876. doi: 10.1152/jn.00835.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 15. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28202574 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational palmitoylation controls the voltage gating and lipid raft association of the CALHM1 channel.J Physiol. 2017 Sep 15;595(18):6121-6145. doi: 10.1113/JP274164. Epub 2017 Aug 14. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28734079 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium homeostasis modulator (CALHM) ion channels.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Mar;468(3):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1757-6. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26603282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conditioned Taste Aversion to L-Amino Acid Taste Stimuli and Oral Transcriptional Changes to Type 1 Taste Receptors T1R1 and T1R3 on Chronic Exposure to L-Alanine Solution in Chickens.J Poult Sci. 2022 Oct 25;59(4):348-356. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0210128. J Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 36382058 Free PMC article.
-
Taste bud formation depends on taste nerves.Elife. 2019 Oct 1;8:e49226. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49226. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31570121 Free PMC article.
-
Spilanthol Enhances Sensitivity to Sodium in Mouse Taste Bud Cells.Chem Senses. 2019 Jan 29;44(2):91-103. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjy069. Chem Senses. 2019. PMID: 30364996 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signaling in the retina: From development to disease.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Sep;151:92-108. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30458250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of candidate genes associated with bacterial and viral infections in wild boars hunted in Tuscany (Italy).Sci Rep. 2022 May 17;12(1):8145. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12353-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35581286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clapp TR, Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon SC, Kinnamon JC. Morphologic characterization of rat taste receptor cells that express components of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Comp Neurol. 2004;468:311–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

