Homogeneous Time Constants Promote Oscillations in Negative Feedback Loops
- PMID: 29676894
- PMCID: PMC6008730
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00442
Homogeneous Time Constants Promote Oscillations in Negative Feedback Loops
Abstract
Biological oscillators are present in nearly all self-regulating systems, from individual cells to entire organisms. In any oscillator structure, a negative feedback loop is necessary, but not sufficient to guarantee the emergence of periodic behaviors. The likelihood of oscillations can be improved by careful tuning of the system time constants and by increasing the loop gain, yet it is unclear whether there is any general relationship between optimal time constants and loop gain. This issue is particularly relevant in genetic oscillators resulting from a chain of different subsequent biochemical events, each with distinct (and uncertain) kinetics. Using two families of genetic oscillators as model examples, we show that the loop gain required for oscillations is minimum when all elements in the loop have the same time constant. On the contrary, we show that homeostasis is ensured if a single element is considerably slower than the others.
Keywords: biomolecular oscillators; delays; feedback; oscillations; synthetic biology; time constants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
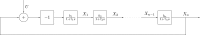
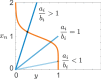
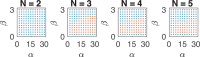
 ; hence, eq 6 is satisfied in the whole
region above. We compute
the solutions of eq 9: red dots indicate an oscillatory behavior, blue dots indicate no
oscillations, while gray dots indicate that no equilibrium can be
found computationally due to numerical problems.
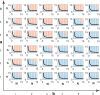
; hence, eq 6 is satisfied in the whole
region above. We compute
the solutions of eq 9: red dots indicate an oscillatory behavior, blue dots indicate no
oscillations, while gray dots indicate that no equilibrium can be
found computationally due to numerical problems.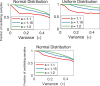
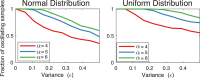
Similar articles
-
Cyclic negative feedback systems: what is the chance of oscillation?Bull Math Biol. 2014 May;76(5):1155-93. doi: 10.1007/s11538-014-9959-1. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Bull Math Biol. 2014. PMID: 24756857
-
Long negative feedback loop enhances period tunability of biological oscillators.J Theor Biol. 2018 Mar 7;440:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2017.12.014. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Theor Biol. 2018. PMID: 29253507
-
The ups and downs of biological oscillators: a comparison of time-delayed negative feedback mechanisms.J R Soc Interface. 2023 Jun;20(203):20230123. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2023.0123. Epub 2023 Jun 28. J R Soc Interface. 2023. PMID: 37376871 Free PMC article.
-
Design principles of biochemical oscillators.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;9(12):981-91. doi: 10.1038/nrm2530. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18971947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic oscillators in development.Dev Growth Differ. 2016 Jan;58(1):16-30. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12262. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Dev Growth Differ. 2016. PMID: 26753997 Review.
Cited by
-
A counter-enzyme complex regulates glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Feb;18(2):161-170. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00919-y. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Nat Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 34931064 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse role of decoys on emergence and precision of oscillations in a biomolecular clock.Biophys J. 2021 Dec 21;120(24):5564-5574. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.11.013. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 34774502 Free PMC article.
-
Loop analysis of blood pressure/volume homeostasis.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Sep 12;15(9):e1007346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007346. eCollection 2019 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31513566 Free PMC article.
-
Computational characterization of recombinase circuits for periodic behaviors.iScience. 2022 Nov 21;26(1):105624. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105624. eCollection 2023 Jan 20. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36619981 Free PMC article.
-
Robustness of a biomolecular oscillator to pulse perturbations.IET Syst Biol. 2020 Jun;14(3):127-132. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2019.0029. IET Syst Biol. 2020. PMID: 32406377 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

