The novel TRAIL-receptor agonist APG350 exerts superior therapeutic activity in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 29670075
- PMCID: PMC5906476
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0478-0
The novel TRAIL-receptor agonist APG350 exerts superior therapeutic activity in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
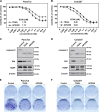
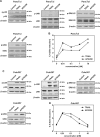
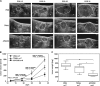
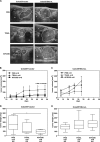
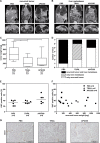
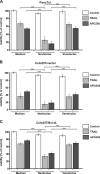
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) has raised attention as a novel anticancer therapeutic as it induces apoptosis preferentially in tumor cells. However, first-generation TRAIL-receptor agonists (TRAs), comprising recombinant TRAIL and agonistic receptor-specific antibodies, have not demonstrated anticancer activity in clinical studies. In fact, cancer cells are often resistant to conventional TRAs. Therefore, in addition to TRAIL-sensitizing strategies, next-generation TRAs with superior apoptotic activity are warranted. APG350 is a novel, highly potent TRAIL-receptor agonist with a hexavalent binding mode allowing the clustering of six TRAIL-receptors per drug molecule. Here we report on preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies testing the activity of APG350 on pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells. We found that APG350 potently induced apoptosis of Colo357, PancTuI and Panc89 cells in vitro. In addition, APG350 treatment activated non-canonical TRAIL signaling pathways (MAPK, p38, JNK, ERK1/ERK2 and NF-κB) and induced the secretion of IL-8. Stable overexpression of Bcl-xL inhibited APG350-induced cell death and augmented activation of non-canonical pathways. Intriguingly, pre-treatment of Bcl-xL-overexpressing cells with the BH3-mimic Navitoclax restored their sensitivity to APG350. To study the effects of APG350 on PDAC cells in vivo, we applied two different orthotopic xenotransplantation mouse models, with and without primary tumor resection, representing adjuvant and palliative treatment regimes, respectively. APG350 treatment of established tumors (palliative treatment) significantly reduced tumor burden. These effects, however, were not seen in tumors with enforced overexpression of Bcl-xL. Upon primary tumor resection and subsequent APG350 treatment (adjuvant therapy), APG350 limited recurrent tumor growth and metastases. Importantly, therapeutic efficacy of APG350 treatment was more effective compared with treatment with soluble TRAIL in both models. In conclusion, APG350 represents a promising next-generation TRA for the treatment of PDAC. Moreover, our results suggest that combining APG350 with Navitoclax might be a succesfull strategy for cancers harboring mitochondrial apoptosis resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
M.K., O.H., C.G. and H.F. are full term employees at APOGENIX AG. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
APG350 induces superior clustering of TRAIL receptors and shows therapeutic antitumor efficacy independent of cross-linking via Fcγ receptors.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Dec;12(12):2735-47. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0323. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 24101228
-
TRAIL-induced expression of uPA and IL-8 strongly enhanced by overexpression of TRAF2 and Bcl-xL in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2013 Feb;12(1):94-8. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(13)60012-0. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2013. PMID: 23392805
-
Hexavalent TRAIL Fusion Protein Eftozanermin Alfa Optimally Clusters Apoptosis-Inducing TRAIL Receptors to Induce On-Target Antitumor Activity in Solid Tumors.Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 15;81(12):3402-3414. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2178. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33687950
-
Impact of death receptor signaling on the malignancy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Jun-Jul;90(6-7):450-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.10.008. Epub 2010 Dec 3. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21129814 Review.
-
TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: Are we on the right TRAIL?Cancer Treat Rev. 2009 May;35(3):280-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009. PMID: 19117685 Review.
Cited by
-
The CD40 agonist HERA-CD40L results in enhanced activation of antigen presenting cells, promoting an anti-tumor effect alone and in combination with radiotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 May 26;14:1160116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1160116. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37304285 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicine in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Status and Future Opportunities for Overcoming Therapy Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 7;13(24):6175. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246175. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Extracellular pH on Apoptotic and Non-Apoptotic TRAIL-Induced Signaling in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 24;10:768579. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.768579. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35281089 Free PMC article.
-
TRAIL-Based Therapies Efficacy in Pediatric Bone Tumors Models Is Modulated by TRAIL Non-Apoptotic Pathway Activation via RIPK1 Recruitment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;14(22):5627. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225627. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428719 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of TRAIL death receptors.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Feb 27;51(1):57-70. doi: 10.1042/BST20220098. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 36629496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Global Cancer Facts & Figures 3rd Edition.Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2015. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

