P190RhoGAP prevents mitotic spindle fragmentation and is required to activate Aurora A kinase at acentriolar poles
- PMID: 29656322
- PMCID: PMC6082689
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-018-0670-0
P190RhoGAP prevents mitotic spindle fragmentation and is required to activate Aurora A kinase at acentriolar poles
Abstract
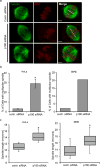
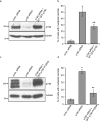
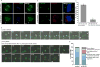
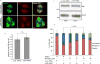
Assembly of the mitotic spindle is essential for proper chromosome segregation during mitosis. Maintenance of spindle poles requires precise regulation of kinesin- and dynein-generated forces, and improper regulation of these forces disrupts pole integrity leading to pole fragmentation. The formation and function of the mitotic spindle are regulated by many proteins, including Aurora A kinase and the motor proteins Kif2a and Eg5. Here, we characterize a surprising role for the RhoA GTPase-activating protein, p190RhoGAP, in regulating the mitotic spindle. We show that cells depleted of p190RhoGAP arrest for long periods in mitosis during which cells go through multiple transitions between having bipolar and multipolar spindles. Most of the p190RhoGAP-depleted cells finally achieve a stable bipolar attachment and proceed through anaphase. The multipolar spindle phenotype can be rescued by low doses of an Eg5 inhibitor. Moreover, we show that p190RhoGAP-depleted multipolar cells localize Aurora A to all the poles, but the kinase is only activated at the two centriolar poles. Overall, our data identify an unappreciated connection between p190RhoGAP and the proteins that control spindle poles including Aurora A kinase and Eg5 that is required to prevent or correct spindle pole fragmentation.
Keywords: Aurora A; Centrosome; Eg5; Mitotic spindle; p190RhoGAP.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors declare that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aurora A, MCAK, and Kif18b promote Eg5-independent spindle formation.Chromosoma. 2017 Aug;126(4):473-486. doi: 10.1007/s00412-016-0607-4. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Chromosoma. 2017. PMID: 27354041 Free PMC article.
-
Tiam1-Rac signaling counteracts Eg5 during bipolar spindle assembly to facilitate chromosome congression.Curr Biol. 2010 Apr 13;20(7):669-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.02.033. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20346677 Free PMC article.
-
CENP-W plays a role in maintaining bipolar spindle structure.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 15;9(10):e106464. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106464. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25329824 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mitotic kinases in coupling the centrosome cycle with the assembly of the mitotic spindle.J Cell Sci. 2014 Oct 1;127(Pt 19):4111-22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.151753. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25128564 Review.
-
Aurora at the pole and equator: overlapping functions of Aurora kinases in the mitotic spindle.Open Biol. 2013 Mar 20;3(3):120185. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120185. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23516109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
p190RhoGAPs, the ARHGAP35- and ARHGAP5-Encoded Proteins, in Health and Disease.Cells. 2019 Apr 12;8(4):351. doi: 10.3390/cells8040351. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31013840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bayliss R, Sardon T, Vernos I, Conti E. Structural basis of Aurora-A activation by TPX2 at the mitotic spindle. Mol Cell. 2003;12(4):851–62. - PubMed
-
- Brouns MR, Matheson SF, Hu KQ, Delalle I, Caviness VS, Silver J, Bronson RT, Settleman J. The adhesion signaling molecule p190 RhoGAP is required for morphogenic processes in normal development. Development. 2000;127:4891–903. - PubMed
-
- Brouns MR, Matheson SF, Settleman J. P190 RhoGAP is the principal Src substrate in brain and regulates axon outgrowth, guidance and fasciculation. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(4):361–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

