N-terminal α-amino group modification of antibodies using a site-selective click chemistry method
- PMID: 29652547
- PMCID: PMC6150616
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1463122
N-terminal α-amino group modification of antibodies using a site-selective click chemistry method
Abstract
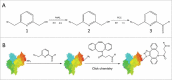
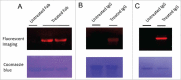
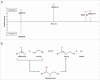
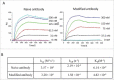
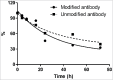
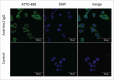
Site-specific conjugation of small molecules to antibody molecules is a promising strategy for generation of antibody-drug conjugates. In this report, we describe the successful synthesis of a novel bifunctional molecule, 6-(azidomethyl)-2-pyridinecarboxyaldehyde (6-AM-2-PCA), which was used for conjugation of small molecules to peptides and antibodies. We demonstrated that 6-AM-2-PCA selectively reacted with N-terminal amino groups of peptides and antibodies. In addition, the azide group of 6-AM-2-PCA enabled copper-free click chemistry coupling with dibenzocyclooctyne-containing reagents. Bifunctional 6-AM-2-PCA mediated site-specific conjugation without requiring genetic engineering of peptides or antibodies. A key advantage of 6-AM-2-PCA as a conjugation reagent is its ability to modify proteins in a single step under physiological conditions that are sufficiently moderate to retain protein function. Therefore, this new click chemistry-based method could be a useful complement to other conjugation methods.
Keywords: Site-specific modification,; antibody; antibody engineering; antibody-drug conjugate; click chemistry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of precision antibody conjugates using proximity-induced chemistry.Theranostics. 2021 Aug 27;11(18):9107-9117. doi: 10.7150/thno.62444. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34522229 Free PMC article.
-
Highly robust and optimized conjugation of antibodies to nanoparticles using quantitatively validated protocols.Nanoscale. 2017 Feb 16;9(7):2548-2555. doi: 10.1039/c6nr04683e. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 28150822
-
Preparation of single- and double-oligonucleotide antibody conjugates and their application for protein analytics.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 29;10(1):1457. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58238-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31996713 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Antibody Conjugation with Payloads beyond Cytotoxins.Molecules. 2023 Jan 17;28(3):917. doi: 10.3390/molecules28030917. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ click chemistry: from small molecule discovery to synthetic antibodies.Integr Biol (Camb). 2013 Jan;5(1):87-95. doi: 10.1039/c2ib20110k. Integr Biol (Camb). 2013. PMID: 22836343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Building Potent Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells With CRISPR Genome Editing.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 19;10:456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00456. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30941126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting B7-H3 Immune Checkpoint With Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered Natural Killer Cells Exhibits Potent Cytotoxicity Against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 30;11:1089. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01089. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32848731 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Antibody Epitope Prediction.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;12(3):52. doi: 10.3390/antib12030052. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37606436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific conjugation of native antibody.Antib Ther. 2020 Dec;3(4):271-284. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbaa027. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Antib Ther. 2020. PMID: 33644685 Free PMC article.
-
Herding cats: Label-based approaches in protein translocation through nanopore sensors for single-molecule protein sequence analysis.iScience. 2021 Aug 25;24(9):103032. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103032. eCollection 2021 Sep 24. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34527891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
