Description of organ-specific phenotype, and functional characteristics of tissue resident lymphocytes from liver transplantation donor and research on immune tolerance mechanism of liver
- PMID: 29643992
- PMCID: PMC5884647
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24514
Description of organ-specific phenotype, and functional characteristics of tissue resident lymphocytes from liver transplantation donor and research on immune tolerance mechanism of liver
Abstract
Aim: Prior to transplantation, Donation after Cardiac Death (DCD) liver transplantation livers are perfused with preservation solution. Therefore, this provides an abundant source of human liver lymphocytes, as well as mesenteric lymph node and spleen for the study of lymphocyte subset diversity in the peripheral blood, lymph node, spleen and liver.
Methods: Lymphocyte subsets were isolated and purified from peripheral blood, lymph node, spleen and liver perfusion, the phenotypic and functional analysis of the tissue resident lymphocyte were performed by flow cytometry.
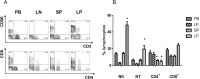
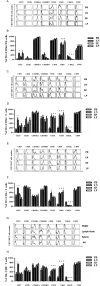
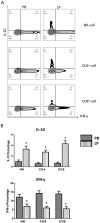
Results: In a direct comparison between blood, liver, lymph node and spleen cells from liver transplantation donors, the abundance of natural killer (NK) cells, CD3+CD56+NKT (NT) cells and CD8+ T cells in intrahapatic lymphocytes (IHL) did not match what was present in peripheral blood and other peripheral lymphoid organs. The activation state of peripheral blood-derived lymphocytes was significantly different from lymph node-, spleen- and liver-derived cells. Intriguingly, NK cells, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells from liver perfusion display more suppressive characteristics, that is, express and produce more anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-10, less inflammatory cytokine interferon (INF)-γ.
Conclusion: Our findings imply that different tissues entail resident lymphocyte subsets with a distinct phenotype and function considering the organ is well vascularized, particularly in liver. It is better to understand the mechanism of liver immune tolerance.
Keywords: intrahepatic lymphocytes; liver immune tolerance; liver transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The spectrum of lymphoid subsets preferentially recruited into the liver reflects that of resident populations.Immunol Lett. 2004 May 15;93(2-3):159-62. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.03.007. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15158612
-
The abundant NK cells in human secondary lymphoid tissues require activation to express killer cell Ig-like receptors and become cytolytic.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1455-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1455. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734722
-
Wall shear stress and intrahepatic leukocytes of graft in living related donor liver transplantation.Hepatogastroenterology. 2004 Mar-Apr;51(56):329-33. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15086151
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Human Circulating and Tissue-Resident CD56(bright) Natural Killer Cell Populations.Front Immunol. 2016 Jun 30;7:262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00262. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27446091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heligmosomoides bakeri and Toxoplasma gondii co-infection leads to increased mortality associated with changes in immune resistance in the lymphoid compartment and disease pathology.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):e0292408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292408. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38950025 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity of Human Hepatic Intrasinusoidal CD56bright Natural Killer Cells against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 28;20(7):1564. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071564. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30925759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blum KS, Pabst R. Lymphocyte numbers and subsets in the human blood. Do they mirror the situation in all organs? Immunol Lett. 2007;108:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2006.10.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olszewski WL. The lymphatic system in body homeostasis: physiological conditions. Lymphat Res Biol. 2003;1:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1089/15396850360495655. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Williams MB, Butcher EC. Homing of naive and memory T lymphocyte subsets to Peyer’s patches, lymph nodes, and spleen. J Immunol. 1997;159:1746–52. - PubMed
-
- Fulgenzi A, Casati R, Colombo FR, Gasparini M, Ferrero E, Bondanza A, Gerundini P, Ferrero ME. Distribution of 99mTc-labeled lymphocytes in control and inflamed rats. Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31:631–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2004.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Westermann J, Söllner S, Ehlers EM, Nohroudi K, Blessenohl M, Kalies K. Analyzing the migration of labeled T cells in vivo: an essential approach with challenging features. Lab Invest. 2003;83:459–69. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.LAB.0000062852.80567.90. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

