Pleiotropic mapping and annotation selection in genome-wide association studies with penalized Gaussian mixture models
- PMID: 29635306
- PMCID: PMC6084565
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty204
Pleiotropic mapping and annotation selection in genome-wide association studies with penalized Gaussian mixture models
Abstract
Motivation: Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified many genetic loci associated with complex traits. A substantial fraction of these identified loci is associated with multiple traits-a phenomena known as pleiotropy. Identification of pleiotropic associations can help characterize the genetic relationship among complex traits and can facilitate our understanding of disease etiology. Effective pleiotropic association mapping requires the development of statistical methods that can jointly model multiple traits with genome-wide single nucleic polymorphisms (SNPs) together.
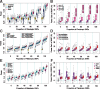
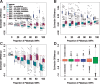
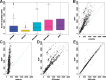
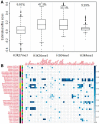
Results: We develop a joint modeling method, which we refer to as the integrative MApping of Pleiotropic association (iMAP). iMAP models summary statistics from GWASs, uses a multivariate Gaussian distribution to account for phenotypic correlation, simultaneously infers genome-wide SNP association pattern using mixture modeling and has the potential to reveal causal relationship between traits. Importantly, iMAP integrates a large number of SNP functional annotations to substantially improve association mapping power, and, with a sparsity-inducing penalty, is capable of selecting informative annotations from a large, potentially non-informative set. To enable scalable inference of iMAP to association studies with hundreds of thousands of individuals and millions of SNPs, we develop an efficient expectation maximization algorithm based on an approximate penalized regression algorithm. With simulations and comparisons to existing methods, we illustrate the benefits of iMAP in terms of both high association mapping power and accurate estimation of genome-wide SNP association patterns. Finally, we apply iMAP to perform a joint analysis of 48 traits from 31 GWAS consortia together with 40 tissue-specific SNP annotations generated from the Roadmap Project.
Availability and implementation: iMAP is freely available at http://www.xzlab.org/software.html.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LSMM: a statistical approach to integrating functional annotations with genome-wide association studies.Bioinformatics. 2018 Aug 15;34(16):2788-2796. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty187. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29608640
-
Improved methods for multi-trait fine mapping of pleiotropic risk loci.Bioinformatics. 2017 Jan 15;33(2):248-255. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw615. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 27663501 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and exploiting trait-relevant tissues with multiple functional annotations in genome-wide association studies.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jan 29;14(1):e1007186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007186. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29377896 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive identification of pleiotropic loci for body fat distribution using the NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies.Obes Rev. 2019 Mar;20(3):385-406. doi: 10.1111/obr.12806. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Obes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30565845 Review.
-
Practical issues in screening and variable selection in genome-wide association analysis.Cancer Inform. 2015 Jan 14;13(Suppl 7):55-65. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S16350. eCollection 2014. Cancer Inform. 2015. PMID: 25635166 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Detection of Potentially Pleiotropic Genes in Coronary Artery Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease Using GWAS Summary Statistics.Front Genet. 2020 Dec 3;11:592461. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.592461. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33343632 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical methods for mediation analysis in the era of high-throughput genomics: Current successes and future challenges.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 May 26;19:3209-3224. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.042. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34141140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coupled mixed model for joint genetic analysis of complex disorders with two independently collected data sets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Feb 5;22(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-03959-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33546598 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian Sparse Mediation Analysis with Targeted Penalization of Natural Indirect Effects.J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 2021 Nov;70(5):1391-1412. doi: 10.1111/rssc.12518. Epub 2021 Sep 12. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat. 2021. PMID: 34887595 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic prediction of complex traits with polygenic scores: a statistical review.Trends Genet. 2021 Nov;37(11):995-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 34243982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B, 57, 289–300.
-
- Bjornsson E. et al. (2017) A rare splice donor mutation in the haptoglobin gene associates with blood lipid levels and coronary artery disease. Hum. Mol. Genet., 26, 2364–2376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

