Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin
- PMID: 29618817
- PMCID: PMC7094983
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0010-9
Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin
Abstract
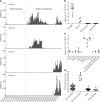
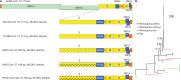
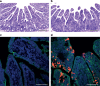
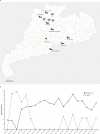
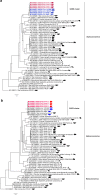
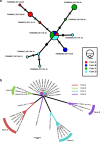
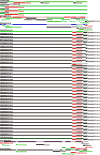
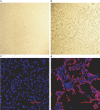
Cross-species transmission of viruses from wildlife animal reservoirs poses a marked threat to human and animal health 1 . Bats have been recognized as one of the most important reservoirs for emerging viruses and the transmission of a coronavirus that originated in bats to humans via intermediate hosts was responsible for the high-impact emerging zoonosis, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) 2-10 . Here we provide virological, epidemiological, evolutionary and experimental evidence that a novel HKU2-related bat coronavirus, swine acute diarrhoea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV), is the aetiological agent that was responsible for a large-scale outbreak of fatal disease in pigs in China that has caused the death of 24,693 piglets across four farms. Notably, the outbreak began in Guangdong province in the vicinity of the origin of the SARS pandemic. Furthermore, we identified SADS-related CoVs with 96-98% sequence identity in 9.8% (58 out of 591) of anal swabs collected from bats in Guangdong province during 2013-2016, predominantly in horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus spp.) that are known reservoirs of SARS-related CoVs. We found that there were striking similarities between the SADS and SARS outbreaks in geographical, temporal, ecological and aetiological settings. This study highlights the importance of identifying coronavirus diversity and distribution in bats to mitigate future outbreaks that could threaten livestock, public health and economic growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Broad Cross-Species Infection of Cultured Cells by Bat HKU2-Related Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus and Identification of Its Replication in Murine Dendritic Cells In Vivo Highlight Its Potential for Diverse Interspecies Transmission.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e01448-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01448-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31554686 Free PMC article.
-
Bat Rhinacoviruses Related to Swine Acute Diarrhoea Syndrome Coronavirus Evolve under Strong Host and Geographic Constraints in China and Vietnam.Viruses. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):1114. doi: 10.3390/v16071114. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066276 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecies Jumping of Bat Coronaviruses.Viruses. 2021 Oct 29;13(11):2188. doi: 10.3390/v13112188. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34834994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bat Coronaviruses in China.Viruses. 2019 Mar 2;11(3):210. doi: 10.3390/v11030210. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30832341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Coronavirus ORF8 Protein Is Acquired from SARS-Related Coronavirus from Greater Horseshoe Bats through Recombination.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10532-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01048-15. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26269185 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pseudorabies Virus Glycoproteins E and B Application in Vaccine and Diagnosis Kit Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;12(9):1078. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12091078. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease tolerance as immune defense strategy in bats: One size fits all?PLoS Pathog. 2024 Sep 5;20(9):e1012471. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012471. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39236038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diversity and cross-species transmissibility of bat-associated picornaviruses from Spain.Virol J. 2024 Aug 22;21(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02456-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39175061 Free PMC article.
-
Global impact of COVID-19 on food safety and environmental sustainability: Pathways to face the pandemic crisis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 24;10(15):e35154. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35154. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the assembly mechanism of SADS-CoV virus nucleocapsid protein: insights from RNA binding, dimerization, and epitope diversity profiling.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0092624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00926-24. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39082816
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

