Impact of CAR Agonist Ligand TCPOBOP on Mouse Liver Chromatin Accessibility
- PMID: 29617930
- PMCID: PMC6016691
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy070
Impact of CAR Agonist Ligand TCPOBOP on Mouse Liver Chromatin Accessibility
Abstract
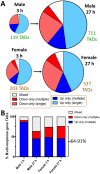
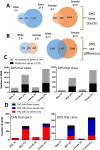
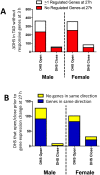
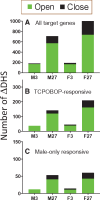
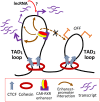
Activation of the nuclear receptor and transcription factor CAR (Nr1i3) by its specific agonist ligand TCPOBOP (1, 4-bis[2-(3, 5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene) dysregulates hundreds of genes in mouse liver and is linked to male-biased hepatocarcinogenesis. To elucidate the genomic organization of CAR-induced gene responses, we investigated the distribution of TCPOBOP-responsive RefSeq coding and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) genes across the megabase-scale topologically associating domains (TADs) that segment the genome, and which provide a structural framework that functionally constrains enhancer-promoter interactions. We show that a subset of TCPOBOP-responsive genes cluster within TADs, and that TCPOBOP-induced genes and TCPOBOP-repressed genes are often found in different TADs. Further, using DNase-seq and DNase hypersensitivity site (DHS) analysis, we identified several thousand genomic regions (ΔDHS) where short-term exposure to TCPOBOP induces localized changes (increases or decreases) in mouse liver chromatin accessibility, many of which cluster in TADs together with TCPOBOP-responsive genes. Sites of chromatin opening were highly enriched nearby genes induced by TCPOBOP and chromatin closing was highly enriched nearby genes repressed by TCPOBOP, consistent with TCPOBOP-responsive ΔDHS serving as enhancers and promoters that positively regulate CAR-responsive genes. Gene expression changes lagged behind chromatin opening or closing for a subset of TCPOBOP-responsive ΔDHS. ΔDHS that were specifically responsive to TCPOBOP in male liver were significantly enriched for genomic regions with a basal male bias in chromatin accessibility; however, the male-biased response of hepatocellular carcinoma-related genes to TCPOBOP was not associated with a correspondingly male-biased ΔDHS response. These studies elucidate the genome-wide organization of CAR-responsive genes and of the thousands of associated genomic sites where TCPOBOP exposure induces both rapid and persistent changes in chromatin accessibility.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Steatotic liver disease induced by TCPOBOP-activated hepatic constitutive androstane receptor: primary and secondary gene responses with links to disease progression.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;200(2):324-345. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae057. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38710495
-
Widespread Epigenetic Changes to the Enhancer Landscape of Mouse Liver Induced by a Specific Xenobiotic Agonist Ligand of the Nuclear Receptor CAR.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Oct 1;171(2):315-338. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz148. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31236583 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Differential Responses of Tumor Promotion-Associated Genes and Dysregulation of Novel Long Noncoding RNAs in Constitutive Androstane Receptor-Activated Mouse Liver.Toxicol Sci. 2017 Sep 1;159(1):25-41. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx114. Toxicol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28903501 Free PMC article.
-
CAR, the continuously advancing receptor, in drug metabolism and disease.Curr Drug Metab. 2005 Aug;6(4):329-39. doi: 10.2174/1389200054633899. Curr Drug Metab. 2005. PMID: 16101572 Review.
-
Chromatin topology in development and disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2019 Apr;55:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 May 21. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2019. PMID: 31125724 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing natural variation to identify cis regulators of sex-biased gene expression in a multi-strain mouse liver model.PLoS Genet. 2021 Nov 9;17(11):e1009588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009588. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34752452 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Growth Hormone Pulses Induce Male-biased Pulsatile Chromatin Opening and Epigenetic Regulation in Adult Mouse Liver.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 16:2023.08.21.554153. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.21.554153. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Dec 13;12:RP91367. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91367 PMID: 37662275 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Plasma growth hormone pulses induce male-biased pulsatile chromatin opening and epigenetic regulation in adult mouse liver.Elife. 2023 Dec 13;12:RP91367. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91367. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38091606 Free PMC article.
-
Steatotic liver disease induced by TCPOBOP-activated hepatic constitutive androstane receptor: primary and secondary gene responses with links to disease progression.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;200(2):324-345. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae057. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38710495
-
Targeting Xenobiotic Nuclear Receptors PXR and CAR to Prevent Cobicistat Hepatotoxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2021 Apr 27;181(1):58-67. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfab023. Toxicol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonev B., Cavalli G. (2016). Organization and function of the 3D genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 17, 661–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

