Regulating Cdc42 and Its Signaling Pathways in Cancer: Small Molecules and MicroRNA as New Treatment Candidates
- PMID: 29596304
- PMCID: PMC6017947
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23040787
Regulating Cdc42 and Its Signaling Pathways in Cancer: Small Molecules and MicroRNA as New Treatment Candidates
Abstract
Despite great improvements in the diagnosis and treatment of neoplasms, metastatic disease is still the leading cause of death in cancer patients, with mortality rates still rising. Given this background, new ways to treat cancer will be important for development of improved cancer control strategies. Cdc42 is a member of the Rho GTPase family and plays an important role in cell-to-cell adhesion, formation of cytoskeletal structures, and cell cycle regulation. It thus influences cellular proliferation, transformation, and homeostasis, as well as the cellular migration and invasion processes underlying tumor formation. Cdc42 acts as a collection point for signal transduction and regulates multiple signaling pathways. Moreover, recent studies show that in most human cancers Cdc42 is abnormally expressed and promoting neoplastic growth and metastasis. Regarding possible new treatments for cancer, miRNA and small molecules targeting Cdc42 and related pathways have been recently found to be effective on cancer. In this review, we analyze the newly recognized regulation mechanisms for Cdc42 and Cdc42-related signal pathways, and particularly new treatments using small molecules and miRNAs to inhibit the abnormal overexpression of Cdc42 that may slow down the metastasis process, improve cancer therapy and lead to novel strategies for development of antineoplastic drugs.
Keywords: Cdc42; Cdc42-related signaling pathways; cancer therapy; miRNAs; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
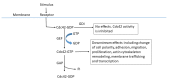
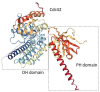
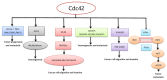
Similar articles
-
Cdc42 Signaling Pathway Inhibition as a Therapeutic Target in Ras- Related Cancers.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(32):3485-3507. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170602082956. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28571533 Review.
-
Cdc42: Role in Cancer Management.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015 Oct;86(4):432-9. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12556. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015. PMID: 25777055 Review.
-
miR-133 is a key negative regulator of CDC42-PAK pathway in gastric cancer.Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2667-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25152372
-
Expression analysis of Cdc42 in lung cancer and modulation of its expression by curcumin in lung cancer cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2012 May;40(5):1561-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1336. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22266952
-
miR-330 regulates the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by targeting Cdc42.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Feb 15;431(3):560-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.016. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23337504
Cited by
-
The differential role of the lipid raft-associated protein flotillin 2 for progression of myeloid leukemia.Blood Adv. 2022 Jun 28;6(12):3611-3624. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005992. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35298613 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cell division control protein 42 in tumor and non-tumor diseases: A systematic review.J Cancer. 2022 Jan 1;13(3):800-814. doi: 10.7150/jca.65415. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35154449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FGD1 Variant Associated With Aarskog-Scott Syndrome.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jul 14;10:888923. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.888923. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35911831 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors in non-small cell lung cancer.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11169-11187. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006519. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34783629 Free PMC article.
-
miR-497 defect contributes to gastric cancer tumorigenesis and progression via regulating CDC42/ITGB1/FAK/PXN/AKT signaling.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Aug 8;25:567-577. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.07.025. eCollection 2021 Sep 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34589278 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

