Good social skills despite poor theory of mind: exploring compensation in autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 29582425
- PMCID: PMC6334505
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpp.12886
Good social skills despite poor theory of mind: exploring compensation in autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
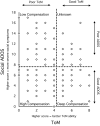
Background: It is proposed that some individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) can 'compensate' for their underlying difficulties (e.g. in theory of mind; ToM), thus demonstrating relatively few behavioural symptoms, despite continued core cognitive deficits. The mechanisms underpinning compensation are largely unexplored, as is its potential impact on mental health. This study aimed to estimate compensation patterns in ASD, by contrasting overt social behaviour with ToM task performance, in order to compare the characteristics of 'Low' and 'High' Compensators.
Methods: A total of 136 autistic adolescents, from the ongoing Social Relationships Study, completed a range of cognitive tasks, the Autistic Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and a self-report anxiety questionnaire. Participants were assigned compensation group status; High Compensators demonstrated good ADOS scores despite poor ToM performance, while Low Compensators demonstrated similarly poor ToM, accompanied by poor ADOS scores.
Results: High Compensators demonstrated better IQ and executive function (EF), but greater self-reported anxiety, compared with Low Compensators. Such differences were not found when comparing individuals who had good versus poor ADOS scores, when ToM performance was good. Other core autistic characteristics (weak central coherence, nonsocial symptoms) did not differentiate the High and Low Compensators.
Conclusions: IQ, EF and anxiety appear to be implicated in the processes by which certain autistic young people can compensate for their underlying ToM difficulties. This tendency to compensate does not appear to reflect the severity of 'hit' for ASD per se, suggesting that well-compensated individuals are not experiencing a milder form of ASD. The construct of compensation in ASD has implications for research and clinical practice.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; adaptation; camouflaging; compensation; compensatory mechanisms; executive function; remediation; theory of mind.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Figures
Comment in
-
Autism's existential crisis: a reflection on Livingston et al. (2018).J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2019 Jan;60(1):111-113. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12989. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30556607
Similar articles
-
Camouflaging in Autism: Examining Sex-Based and Compensatory Models in Social Cognition and Communication.Autism Res. 2021 Jan;14(1):127-142. doi: 10.1002/aur.2440. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Autism Res. 2021. PMID: 33220170 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring links between language and cognition in autism spectrum disorders: Complement sentences, false belief, and executive functioning.J Commun Disord. 2015 Mar-Apr;54:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2014.12.001. Epub 2015 Jan 6. J Commun Disord. 2015. PMID: 25637130
-
The Influence of Premorbid Adjustment and Autistic Traits on Social Cognitive Dysfunction in Schizophrenia.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2020 Mar;26(3):276-285. doi: 10.1017/S1355617719000961. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2020. PMID: 31507263
-
Neurocognitive considerations when assessing Theory of Mind in Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2016 Oct;28(3):233-241. doi: 10.2989/17280583.2016.1268141. J Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2016. PMID: 27998262 Review.
-
[Social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder: Points of convergence and functional differences].Encephale. 2018 Dec;44(6):523-537. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Encephale. 2018. PMID: 30122298 Review. French.
Cited by
-
How Does Understanding of Social Situations and Other's Intention Contribute to Idiom and Irony Comprehension in Autism Spectrum Disorder?Brain Sci. 2024 Oct 18;14(10):1034. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14101034. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39452047 Free PMC article.
-
Non-suicidal self-injury and its relation to suicide through acquired capability: investigating this causal mechanism in a mainly late-diagnosed autistic sample.Mol Autism. 2022 Nov 12;13(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13229-022-00522-5. Mol Autism. 2022. PMID: 36371252 Free PMC article.
-
A robot or a dumper truck? Facilitating play-based social learning across neurotypes.Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2022 Mar 21;7:23969415221086714. doi: 10.1177/23969415221086714. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Autism Dev Lang Impair. 2022. PMID: 36382066 Free PMC article.
-
The Experiences of Autistic People When Facemask Wearing and Interacting with Masked Individuals.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Jun 17;6(2):162-176. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0091. eCollection 2024 Jun. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 39139512
-
Compensatory strategies below the behavioural surface in autism: a qualitative study.Lancet Psychiatry. 2019 Sep;6(9):766-777. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30224-X. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31350208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abell, F. , Happé, F. , & Frith, U. (2000). Do triangles play tricks? Attribution of mental states to animated shapes in normal and abnormal development. Cognitive Development, 15, 1–16.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th edn). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Anzures, G. , Goyet, L. , Ganea, N. , & Johnson, M.H. (2016). Enhanced ERPs to visual stimuli in unaffected male siblings of ASD children. Child Neuropsychology, 22, 220–237. - PubMed
-
- Baron‐Cohen, S. , Wheelwright, S. , Hill, J. , Raste, Y. , & Plumb, I. (2001). The “Reading the Mind in the Eyes” Test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger Syndrome or high‐functioning autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42, 241–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

