Enhancing the accuracy of next-generation sequencing for detecting rare and subclonal mutations
- PMID: 29576615
- PMCID: PMC6485430
- DOI: 10.1038/nrg.2017.117
Enhancing the accuracy of next-generation sequencing for detecting rare and subclonal mutations
Abstract
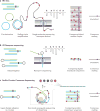
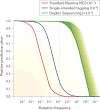
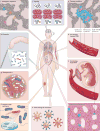
Mutations, the fuel of evolution, are first manifested as rare DNA changes within a population of cells. Although next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have revolutionized the study of genomic variation between species and individual organisms, most have limited ability to accurately detect and quantify rare variants among the different genome copies in heterogeneous mixtures of cells or molecules. We describe the technical challenges in characterizing subclonal variants using conventional NGS protocols and the recent development of error correction strategies, both computational and experimental, including consensus sequencing of single DNA molecules. We also highlight major applications for low-frequency mutation detection in science and medicine, describe emerging methodologies and provide our vision for the future of DNA sequencing.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Applying next-generation sequencing to unravel the mutational landscape in viral quasispecies.Virus Res. 2020 Jul 2;283:197963. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197963. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32278821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A system for detecting high impact-low frequency mutations in primary tumors and metastases.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 11;37(2):185-196. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.322. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28892047 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Event Detection Using Error-corrected DNA and RNA Sequencing.J Vis Exp. 2018 Aug 3;(138):57509. doi: 10.3791/57509. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30124656 Free PMC article.
-
Significance and limitations of the use of next-generation sequencing technologies for detecting mutational signatures.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Nov;107:103200. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103200. Epub 2021 Aug 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34411908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detecting Rare Mutations and DNA Damage with Sequencing-Based Methods.Trends Biotechnol. 2018 Jul;36(7):729-740. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Trends Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29550161 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Somatic mutation landscapes at single-molecule resolution.Nature. 2021 May;593(7859):405-410. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03477-4. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33911282
-
Ultrasensitive detection of genetic variation based on dual signal amplification assisted by isothermal amplification and cobalt oxyhydroxide nanosheets/quantum dots.Mikrochim Acta. 2023 Dec 8;191(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s00604-023-06097-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2023. PMID: 38063936
-
The Clinical Versatility of Next-Generation Sequencing in Colorectal Cancer.Am J Biomed Sci Res. 2020;7(6):548-550. doi: 10.34297/ajbsr.2020.07.001220. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Am J Biomed Sci Res. 2020. PMID: 32924015 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the performance of low-frequency variant calling tools for the detection of variants from short-read deep sequencing data.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 22;13(1):20444. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47135-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37993475 Free PMC article.
-
Detection methods and prognosis implications of measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia.Ann Hematol. 2024 Dec;103(12):4869-4881. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-06008-z. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 39283479 Review.
References
-
- Darwin C. On the origin of species. John Murray Press; 1859.
-
- Cairns J. Mutation selection and the natural history of cancer. Nature. 1975;255:197–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

