Dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through α2AR/PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 29566706
- PMCID: PMC5865375
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1455-1
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through α2AR/PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury caused by renal ischemia-reperfusion is one of the leading causes of acute kidney injury-related death. Dexmedetomidine, an α2-adrenergic agonist sedative, has been found to have protective effects against acute kidney injury and remote lung injury. We sought to determine whether dexmedetomidine can exert its anti-apoptotic effects in acute lung injury after acute kidney injury, in addition to its common anti-inflammatory effects, and to determine the underlying mechanisms.
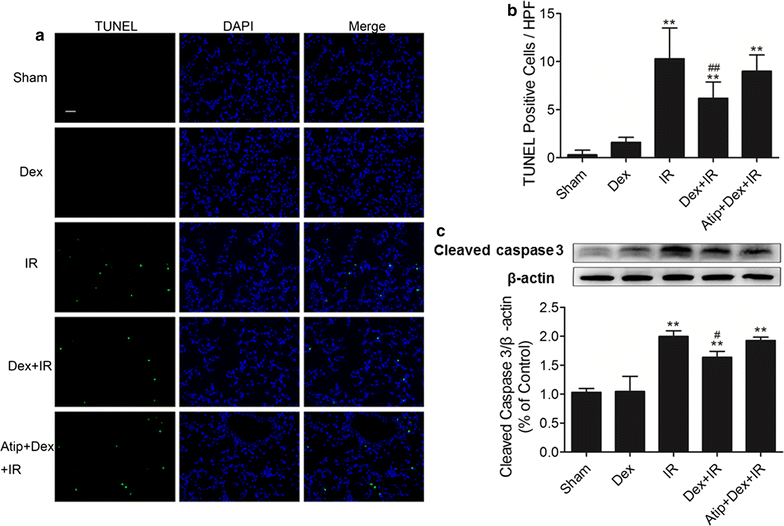
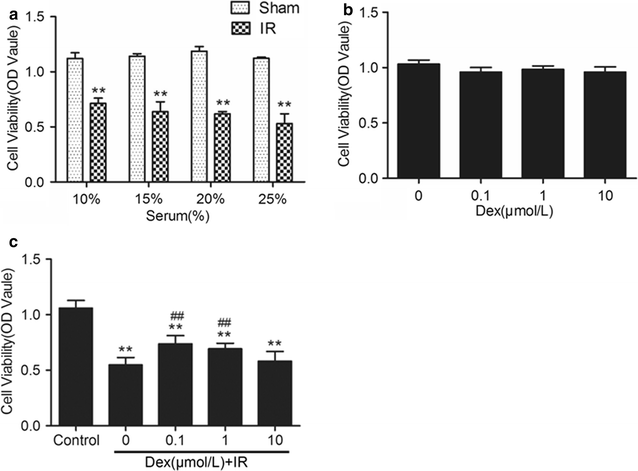
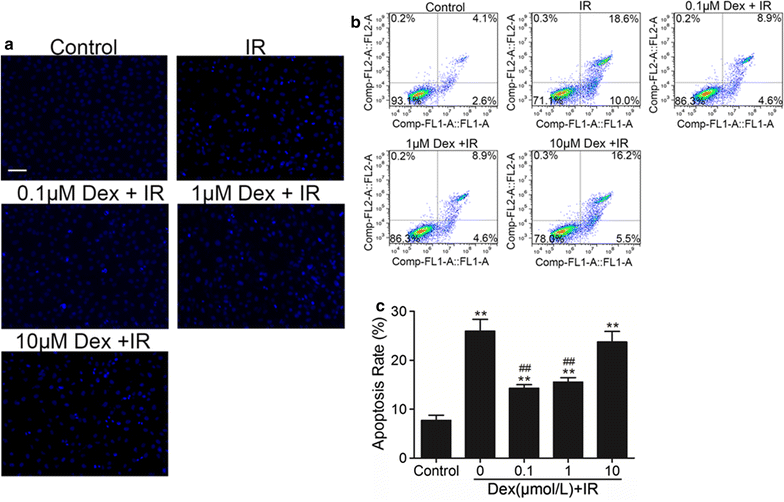
Methods: In vivo, acute kidney injury was induced by 60 min of kidney ischemia (bilateral occlusion of renal pedicles) followed by 24 h of reperfusion. Mice received dexmedetomidine (25 µg/kg, i.p.) in the absence or presence of α2-adrenergic antagonist atipamezole (250 µg/kg, i.p.) before IR. Histological assessment of the lung was conducted by HE staining and arterial blood gases were measured. Lung apoptosis was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling assay. The expression of caspase 3 and p-Akt in lung tissue was detected by western blot. In vitro, C57BL/6J mice pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells were treated with serum from mice obtained following sham or IR. Dexmedetomidine was given before serum stimulation in cells, alone or with atipamezole or LY294002. Cell viability was assessed by CCK 8 assay. Cell apoptosis was examined by Hoechst staining and Annexin V-FITC/PI staining flow cytometry analysis. Mitochondrial membrane potential was measured by flow cytometry. The expression of p-Akt, caspase 3, Bcl-2 and Bax was measured by western blot.
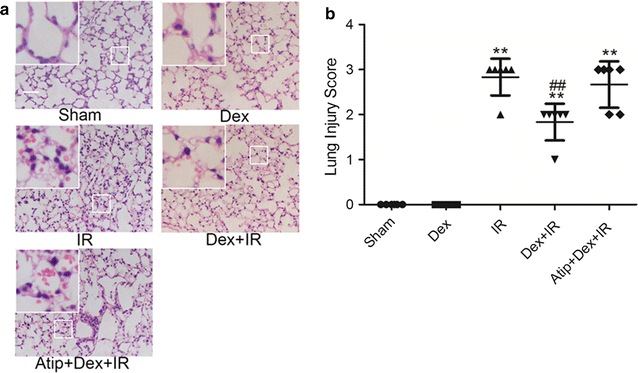
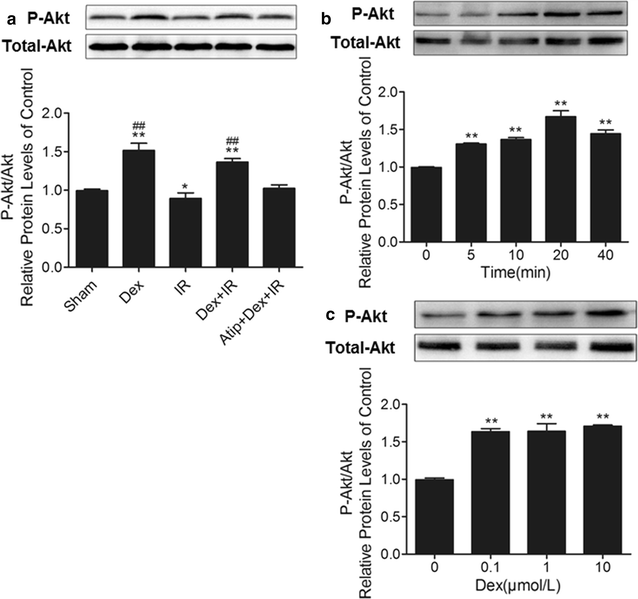
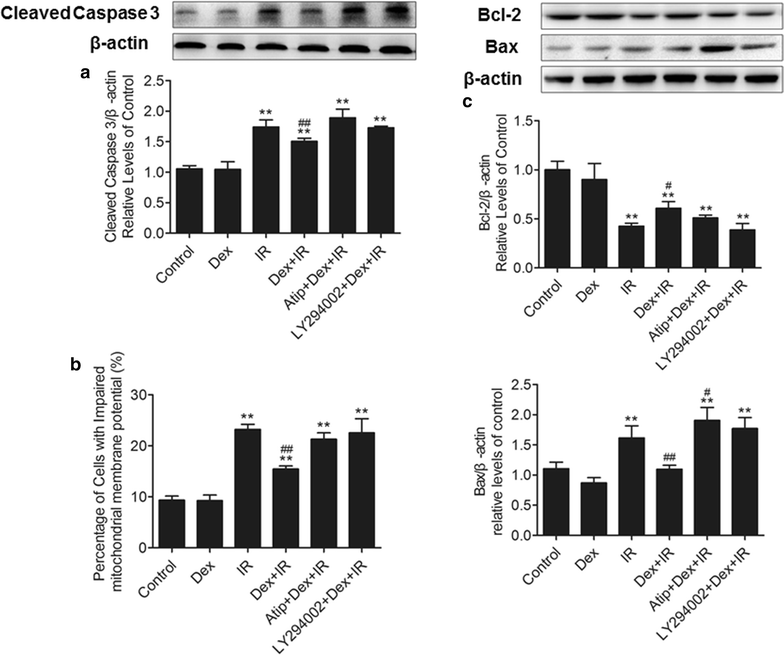
Results: In vivo, dexmedetomidine remarkably mitigated pathohistological changes and apoptosis and significantly increased p-Akt expression in the lung. In addition, dexmedetomidine also slightly improved oxygenation in mice after IR, which can be abolished by atipamezole. In vitro, dexmedetomidine significantly inhibited IR serum-induced loss of viability and apoptosis in PMVECs. Dexmedetomidine increased p-Akt in a time- and dose-dependent manner, and down-regulated the expression of caspase 3 and Bax and up-regulated the Bcl-2 expression in PMVECs. The changes of MMP were also improved by dexmedetomidine. Whilst these effects were abolished by Atipamezole or LY294002.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by IR, at least in part, via α2AR/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Akt pathway; Apoptosis; Renal ischemia–reperfusion; α2-Adrenoceptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
α2-adrenoreceptor modulated FAK pathway induced by dexmedetomidine attenuates pulmonary microvascular hyper-permeability following kidney injury.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 30;7(35):55990-56001. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10809. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27463003 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates cisplatin‑induced acute kidney injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress‑induced apoptosis via the α2AR/PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):1597-1605. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10962. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016445 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates Post-CPB Lung Injury in Rats by Activating the PI3K/Akt Pathway.J Invest Surg. 2020 Jul;33(6):576-583. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2018.1529839. Epub 2019 Mar 26. J Invest Surg. 2020. PMID: 30913929
-
Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: a narrative review.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Feb;11(2):806-817. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3286. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 35016518 Review.
-
Perioperative acute kidney injury: The renoprotective effect and mechanism of dexmedetomidine.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Feb 5;695:149402. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.149402. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38159412 Review.
Cited by
-
Tanshinone IIA combined with CsA inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in obese rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Mar 22;21(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03270-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33752661 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo and in vitro by preserving mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium through the HIF-1a/HO-1 signaling pathway.Redox Biol. 2021 May;41:101954. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101954. Epub 2021 Mar 21. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 33774474 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine post-treatment attenuates cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting apoptosis through HIF-1α signalling.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(1):850-861. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14795. Epub 2019 Nov 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31680420 Free PMC article.
-
α2A-Adrenergic Receptor Inhibits the Progression of Cervical Cancer Through Blocking PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 15;13:10535-10546. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S264409. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33116632 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway.J Anesth. 2021 Jun;35(3):394-404. doi: 10.1007/s00540-021-02909-9. Epub 2021 Apr 5. J Anesth. 2021. PMID: 33821300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeh JH, Yang YC, Wang JC, Wang D, Wang JJ. Curcumin attenuates renal ischemia and reperfusion injury–induced restrictive respiratory insufficiency. In: Transplantation proceedings, vol. 45. 2013. p. 3542–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

