The interplay of reactive oxygen species and the epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor progression and drug resistance
- PMID: 29548337
- PMCID: PMC5857086
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0728-0
The interplay of reactive oxygen species and the epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor progression and drug resistance
Abstract
Background: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays important roles in cell survival, growth, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. Dysregulation of the EGFR is a common mechanism in cancer progression especially in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
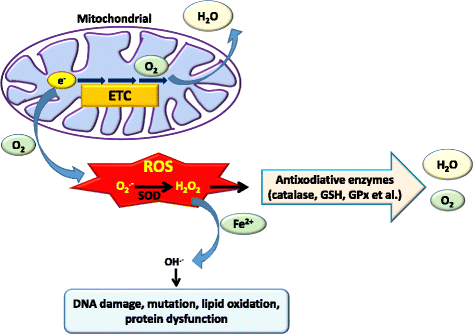
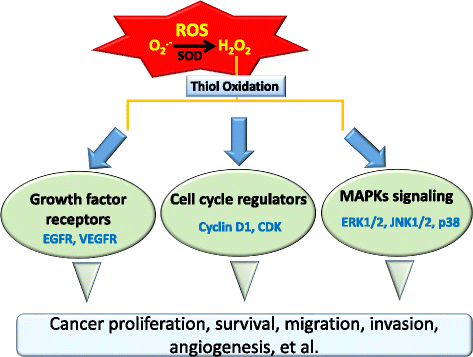
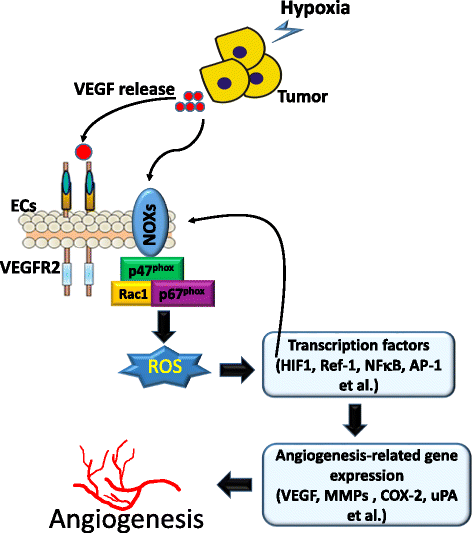
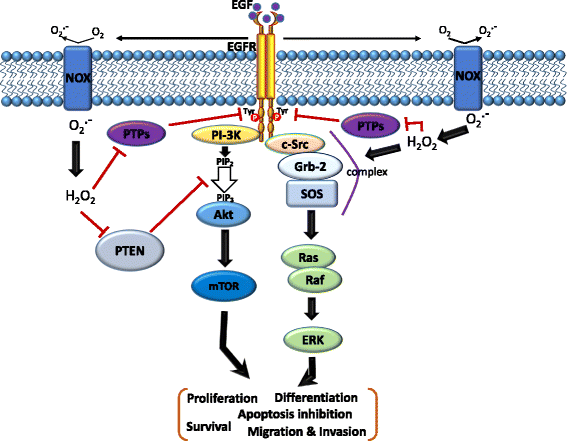
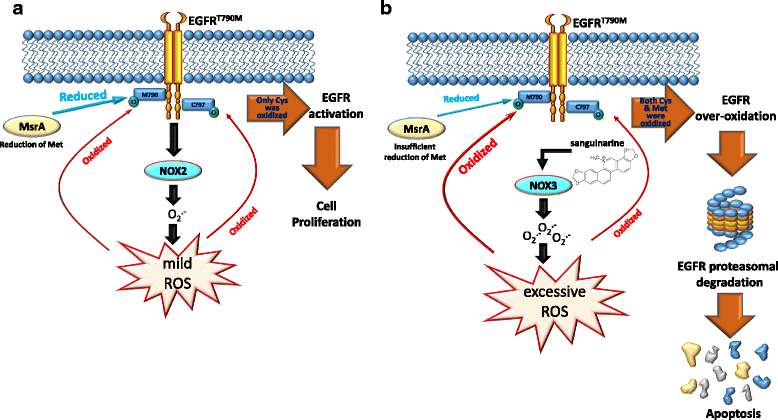
Main body: Suppression of the EGFR-mediated signaling pathway is used in cancer treatment. Furthermore, reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced oxidative stress from mitochondrial dysfunction or NADPH oxidase (NOX) overactivation and ectopic expression of antioxidative enzymes were also indicated to be involved in EGFR-mediated tumor progression (proliferation, differentiation, migration, and invasion) and drug resistance (EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)). The products of NOX, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, are considered to be major types of ROS. ROS are not only toxic materials to cells but also signaling regulators of tumor progression. Oxidation of both the EGFR and downstream phosphatases by ROS enhances EGFR-mediated signaling and promotes tumor progression. This review primarily focuses on the recent literature with respect to the roles of the EGFR and ROS and correlations between ROS and the EGFR in tumor progression and EGFR TKI resistance.
Short conclusion: The evidence discussed in this article can serve as a basis for basic and clinical research to understand how to modulate ROS levels to control the development and drug resistance of cancers.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Epidermal growth factor receptor; NADPH oxidase; Oxidation; Reactive oxygen species; Tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Inducing Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Degradation via Methionine 790 Oxidation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Feb 10;24(5):263-79. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6420. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26528827 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired Resistance of EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment Promotes PARP Inhibitor Sensitivity.Cell Rep. 2019 Jun 18;27(12):3422-3432.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.058. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31216465 Free PMC article.
-
Combination treatment with erlotinib and ampelopsin overcomes erlotinib resistance in NSCLC cells via the Nox2-ROS-Bim pathway.Lung Cancer. 2017 Apr;106:115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28285685
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0777-1. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between exposure to organophosphate flame retardants and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in lung cancer patients.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Aug;15(24):1805-1814. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15411. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39045786 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a redox-related gene signature for overall survival prediction and immune infiltration in non-small-cell lung cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 16;9:942402. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.942402. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36052170 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced EGFR Level in eIF2α PhosphorylationDeficient Hepatocytes Is Responsible for Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress.Mol Cells. 2020 Mar 31;43(3):264-275. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2020.2197. Mol Cells. 2020. PMID: 32150794 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Orchestrates MAPK and Nitric-Oxide Synthase Signal.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 19;21(22):8750. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228750. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33228180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoting reactive oxygen species accumulation to overcome tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03418-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38982494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

