SIRT1 Deacetylates Tau and Reduces Pathogenic Tau Spread in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy
- PMID: 29540553
- PMCID: PMC5895994
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2369-17.2018
SIRT1 Deacetylates Tau and Reduces Pathogenic Tau Spread in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Min et al., "SIRT1 Deacetylates Tau and Reduces Pathogenic Tau Spread in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy".J Neurosci. 2023 Apr 12;43(15):2817. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0439-23.2023. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36977588 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
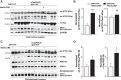
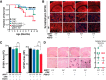
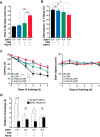
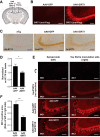
Hyperacetylation of tau has been implicated in neurodegeneration and cognitive decline in tauopathy brains. The nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide-dependent class-III protein deacetylase SIRT1 is one of the major enzymes involved in removal of acetyl groups from tau in vitro However, whether SIRT1 regulates acetylation of pathogenic tau and ameliorates tau-mediated pathogenesis remains unclear. Here, we report deacetylating activity of SIRT1 for acetylated Lys174 (K174) of tau in tauP301S transgenic mice with a brain-specific SIRT1 deletion. We show that SIRT1 deficiency leads to exacerbation of premature mortality, synapse loss, and behavioral disinhibition in tauP301S transgenic mice of both sexes. By contrast, SIRT1 overexpression by stereotaxic delivery of adeno-associated virus that encodes SIRT1 into the hippocampus reduces acetylated K174 tau. Furthermore, SIRT1 overexpression significantly attenuates the spread of tau pathology into anatomically connected brain regions of tauP301S transgenic mice of both sexes. These findings suggest the functional importance of SIRT1 in regulating pathogenic tau acetylation and in suppressing the spread of tau pathology in vivoSIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT In neurodegenerative disorders with inclusions of microtubule-associated protein tau, aberrant lysine acetylation of tau plays critical roles in promoting tau accumulation and toxicity. Identifying strategies to deacetylate tau could interfere with disease progression; however, little is known about how pathogenic tau is deacetylated in vivo Here we show that the protein deacetylase SIRT1 reduces tau acetylation in a mouse model of neurodegeneration. SIRT1 deficiency in the brain aggravates synapse loss and behavioral disinhibition, and SIRT1 overexpression ameliorates propagation of tau pathology.
Keywords: SIRT1; acetylation; dementia; tau; tau spread.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/383680-09$15.00/0.
Figures

Comment in
-
SIRT1: A Novel Way to Target Tau?J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 5;38(36):7755-7757. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1201-18.2018. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30185537 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Acetylation of tau inhibits its degradation and contributes to tauopathy.Neuron. 2010 Sep 23;67(6):953-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.044. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20869593 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylated tau inhibits chaperone-mediated autophagy and promotes tau pathology propagation in mice.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 14;12(1):2238. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22501-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33854069 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 Deacetylates SC35 and Suppresses Its Function in Tau Exon 10 Inclusion.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(2):561-570. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170418. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29226865
-
Acetylated tau in Alzheimer's disease: An instigator of synaptic dysfunction underlying memory loss: Increased levels of acetylated tau blocks the postsynaptic signaling required for plasticity and promotes memory deficits associated with tauopathy.Bioessays. 2017 Apr;39(4):10.1002/bies.201600224. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600224. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Bioessays. 2017. PMID: 28083916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tauopathies as clinicopathological entities.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Jan;22 Suppl 1(0 1):S29-33. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.09.020. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26382841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of altered protein acetylation in neurodegenerative disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;14:1025473. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1025473. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36688174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 Is Involved in the Neuroprotection of Pterostilbene Against Amyloid β 25-35-Induced Cognitive Deficits in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 14;13:877098. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.877098. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35496289 Free PMC article.
-
Glimepiride mitigates tauopathy and neuroinflammation in P301S transgenic mice: role of AKT/GSK3β signaling.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Oct;30(5):1871-1890. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01023-w. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35922737 Free PMC article.
-
TSC1 loss increases risk for tauopathy by inducing tau acetylation and preventing tau clearance via chaperone-mediated autophagy.Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 5;7(45):eabg3897. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg3897. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34739309 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Approaches for the Treatment of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 8;20(3):719. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030719. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30743990 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barghorn S, Biernat J, Mandelkow E (2005) Purification of recombinant tau protein and preparation of Alzheimer-paired helical filaments in vitro. Methods Mol Biol 299:35–51. - PubMed
-
- Cho SH, Chen JA, Sayed F, Ward ME, Gao F, Nguyen TA, Krabbe G, Sohn PD, Lo I, Minami S, Devidze N, Zhou Y, Coppola G, Gan L (2015) SIRT1 deficiency in microglia contributes to cognitive decline in aging and neurodegeneration via epigenetic regulation of IL-1β. J Neurosci 35:807–818. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2939-14.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
