G Protein α Subunit GpaB is Required for Asexual Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity by Regulating cAMP Signaling in Aspergillus flavus
- PMID: 29534423
- PMCID: PMC5869405
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10030117
G Protein α Subunit GpaB is Required for Asexual Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity by Regulating cAMP Signaling in Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
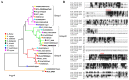
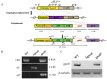
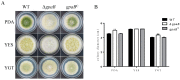
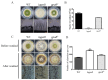
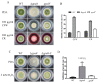
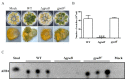
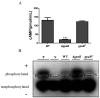
The heterotrimeric G proteins are critical for signal transduction and function in numerous biological processes including vegetative growth, asexual development and fungal virulence in fungi. Here, we identified four G protein alpha subunits (GanA, GpaB, FadA and GaoC) in the notorious Aflatoxin-producing fungus Aspergillus flavus. GanA, GpaB and FadA have homologues in other fungal species, while GaoC is a novel one. Here, we showed that the loss function of gpaB displayed a defect in conidiophore formation and considerably reduced expression levels of conidia-specific genes brlA and abaA. A decreased viability of cell wall integrity stress and oxidative stress were also found in the ∆gpaB mutant. More importantly, aflatoxin (AF) biosynthesis and infection on crop seeds were severely impaired in the gpaB-deficient mutant. Further analyses demonstrated that the intracellular cAMP levels significantly reduced in the gpaB-deficient mutant compared to wildtype strains. Additionally, an alteration of PKA activities in the ∆gpaB mutant was also found. Overall, our results indicated that GpaB played diverse roles in asexual sporulation, AF biosynthesis and virulence by regulating cAMP signaling in Aspergillus flavus.
Keywords: G protein; cAMP; fungal virulence; sclerotia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulator of G Protein Signaling Contributes to the Development and Aflatoxin Biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus through the Regulation of Gα Activity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jun 28;88(12):e0024422. doi: 10.1128/aem.00244-22. Epub 2022 May 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. Retraction in: Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Mar 29;89(3):e0201122. doi: 10.1128/aem.02011-22 PMID: 35638847 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Adenylate Cyclase AcyA Regulates Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis and Fungal Virulence in Aspergillus flavus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Dec 21;6:190. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00190. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 28066725 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclase-Associated Protein Cap with Multiple Domains Contributes to Mycotoxin Biosynthesis and Fungal Virulence in Aspergillus flavus.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 Apr 17;67(15):4200-4213. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07115. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30916945
-
Regulation of Conidiogenesis in Aspergillus flavus.Cells. 2022 Sep 7;11(18):2796. doi: 10.3390/cells11182796. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36139369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the genetics of regulation of aflatoxin production and Aspergillus flavus development.Mycopathologia. 2006 Sep;162(3):155-66. doi: 10.1007/s11046-006-0050-9. Mycopathologia. 2006. PMID: 16944283 Review.
Cited by
-
FFGA1 Protein Is Essential for Regulating Vegetative Growth, Cell Wall Integrity, and Protection against Stress in Flammunina filiformis.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;8(4):401. doi: 10.3390/jof8040401. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448632 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Two G-Protein α Subunits in Vegetative Growth, Cell Wall Integrity, and Virulence of the Entomopathogenic Fungus Metarhizium robertsii.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;8(2):132. doi: 10.3390/jof8020132. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205884 Free PMC article.
-
Host-Induced Gene Silencing of a G Protein α Subunit Gene CsGpa1 Involved in Pathogen Appressoria Formation and Virulence Improves Tobacco Resistance to Ciboria shiraiana.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;7(12):1053. doi: 10.3390/jof7121053. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947035 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G Protein Signaling Contributes to the Development and Aflatoxin Biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus through the Regulation of Gα Activity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jun 28;88(12):e0024422. doi: 10.1128/aem.00244-22. Epub 2022 May 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. Retraction in: Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Mar 29;89(3):e0201122. doi: 10.1128/aem.02011-22 PMID: 35638847 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Transcriptomic Insights into Benzenamine Effects on the Development, Aflatoxin Biosynthesis, and Virulence of Aspergillus flavus.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jan 27;11(2):70. doi: 10.3390/toxins11020070. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30691218 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

