Overview of refinement procedures within REFMAC5: utilizing data from different sources
- PMID: 29533229
- PMCID: PMC5947762
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798318000979
Overview of refinement procedures within REFMAC5: utilizing data from different sources
Abstract
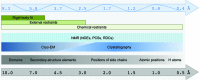
Refinement is a process that involves bringing into agreement the structural model, available prior knowledge and experimental data. To achieve this, the refinement procedure optimizes a posterior conditional probability distribution of model parameters, including atomic coordinates, atomic displacement parameters (B factors), scale factors, parameters of the solvent model and twin fractions in the case of twinned crystals, given observed data such as observed amplitudes or intensities of structure factors. A library of chemical restraints is typically used to ensure consistency between the model and the prior knowledge of stereochemistry. If the observation-to-parameter ratio is small, for example when diffraction data only extend to low resolution, the Bayesian framework implemented in REFMAC5 uses external restraints to inject additional information extracted from structures of homologous proteins, prior knowledge about secondary-structure formation and even data obtained using different experimental methods, for example NMR. The refinement procedure also generates the `best' weighted electron-density maps, which are useful for further model (re)building. Here, the refinement of macromolecular structures using REFMAC5 and related tools distributed as part of the CCP4 suite is discussed.
Keywords: LORESTR; NMR restraints; ProSMART; REFMAC5; refinement.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low Resolution Refinement of Atomic Models Against Crystallographic Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:565-593. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7000-1_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28573589 Review.
-
Neutron crystallographic refinement with REFMAC5 from the CCP4 suite.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2023 Dec 1;79(Pt 12):1056-1070. doi: 10.1107/S2059798323008793. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37921806 Free PMC article.
-
REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011 Apr;67(Pt 4):355-67. doi: 10.1107/S0907444911001314. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011. PMID: 21460454 Free PMC article.
-
GEMMI and Servalcat restrain REFMAC5.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2023 May 1;79(Pt 5):368-373. doi: 10.1107/S2059798323002413. Epub 2023 May 4. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37158197 Free PMC article.
-
Current approaches for the fitting and refinement of atomic models into cryo-EM maps using CCP-EM.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Jun 1;74(Pt 6):492-505. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318007313. Epub 2018 May 30. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29872001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A structural role for tryptophan in proteins, and the ubiquitous Trp Cδ1-H...O=C (backbone) hydrogen bond.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024 Jul 1;80(Pt 7):551-562. doi: 10.1107/S2059798324005515. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38941144 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio cholerae SpeG Spermidine/Spermine N-Acetyltransferase Allosteric Loop and β6-β7 Structural Elements Are Critical for Kinetic Activity.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 13;8:645768. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.645768. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33928120 Free PMC article.
-
The Parallel Presentation of Two Functional CTL Epitopes Derived from the O and Asia 1 Serotypes of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus and Swine SLA-2*HB01: Implications for Universal Vaccine Development.Cells. 2022 Dec 12;11(24):4017. doi: 10.3390/cells11244017. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552780 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of an extracellular superoxide dismutase from Onchocerca volvulus and implications for parasite-specific drug development.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2022 Jun 1;78(Pt 6):232-240. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X22005350. Epub 2022 May 27. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35647680 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalency of nucleosome recognition by LEDGF.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Oct 13;51(18):10011-10025. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad674. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37615563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

