H2A.Z regulates tumorigenesis, metastasis and sensitivity to cisplatin in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 29532867
- PMCID: PMC5843396
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4292
H2A.Z regulates tumorigenesis, metastasis and sensitivity to cisplatin in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
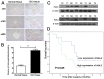
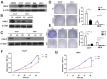
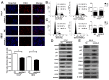
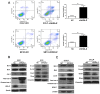
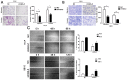
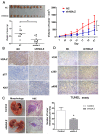
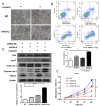
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a fatal, malignant tumor of the liver; effective diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for ICC have not been identified yet. High expression of H2A histone family member Z (H2A.Z) is a high-risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer and primary hepatocellular cancer. However, the significance of H2A.Z and its expression in ICC remains unknown. The present study demonstrated that H2A.Z is overexpressed in ICC and expression of H2A.Z correlated with poor prognosis in patients with ICC. H2A.Z regulated cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via H2A.Z/S-phase kinase-associated protein 2/p27/p21 signaling. Inhibition of H2A.Z reduced cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in ICC. In addition, downregulation of H2AZ reduced tumor metastasis by repressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhanced the antitumor effects of cisplatin in the treatment of ICC. Overall, H2A.Z promoted cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ICC, suggesting that H2A.Z may be a novel biomarker and therapeutic target for ICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
YBX1 promotes stemness and cisplatin insensitivity in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via the AKT/β-catenin axis.J Gene Med. 2024 May;26(5):e3689. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3689. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 38676365
-
MiR-21 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma proliferation and growth in vitro and in vivo by targeting PTPN14 and PTEN.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):5932-46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3465. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25803229 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP4A1 promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75210-75220. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12116. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655691 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple cellular origins and molecular evolution of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2016 Sep 1;379(2):253-61. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.02.038. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26940139 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jan;21(1):177-184. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12951. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27619971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low Magnetic Field Exposure Alters Prostate Cancer Cell Properties.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;13(9):734. doi: 10.3390/biology13090734. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336161 Free PMC article.
-
The novel epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins and their therapeutic targets in cholangiocarcinoma: a narrative review.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jun 30;14(3):1593-1612. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-1126. Epub 2023 May 26. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37435208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive bioinformatic analysis reveals oncogenic role of H2A.Z isoforms in cervical cancer progression.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Nov;24(11):1470-1481. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.58287.. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35317119 Free PMC article.
-
ANP32e Binds Histone H2A.Z in a Cell Cycle-Dependent Manner and Regulates Its Protein Stability in the Cytoplasm.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(2):72-85. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2319731. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38482865 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian PERIOD2 regulates H2A.Z incorporation in chromatin to orchestrate circadian negative feedback.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Jun;29(6):549-562. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00777-9. Epub 2022 May 23. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35606517
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

