Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes
- PMID: 29531354
- PMCID: PMC5968830
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0058-3
Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes.Nat Genet. 2019 Jul;51(7):1192-1193. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0449-0. Nat Genet. 2019. PMID: 31160810
Abstract
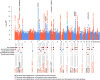
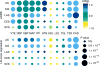
Stroke has multiple etiologies, but the underlying genes and pathways are largely unknown. We conducted a multiancestry genome-wide-association meta-analysis in 521,612 individuals (67,162 cases and 454,450 controls) and discovered 22 new stroke risk loci, bringing the total to 32. We further found shared genetic variation with related vascular traits, including blood pressure, cardiac traits, and venous thromboembolism, at individual loci (n = 18), and using genetic risk scores and linkage-disequilibrium-score regression. Several loci exhibited distinct association and pleiotropy patterns for etiological stroke subtypes. Eleven new susceptibility loci indicate mechanisms not previously implicated in stroke pathophysiology, with prioritization of risk variants and genes accomplished through bioinformatics analyses using extensive functional datasets. Stroke risk loci were significantly enriched in drug targets for antithrombotic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Gretarsdottir, G.T., U.T., and K.S. are all employees of deCODE Genetics/Amgen, Inc. M.A.N. is an employee of Data Tecnica International. P.T.E. is the PI on a grant from Bayer HealthCare to the Broad Institute, focused on the genetics and therapeutics of atrial fibrillation. S.A.L. receives sponsored research support from Bayer HealthCare, Biotronik, and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has consulted for St. Jude Medical and Quest Diagnostics. E.I. is a scientific advisor for Precision Wellness, Cellink and Olink Proteomics for work unrelated to the present project. B.M.P. serves on the DSMB of a clinical trial funded by Zoll LifeCor and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. The remaining authors have no disclosures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic variations and risk of placental abruption: A genome-wide association study and meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies.Placenta. 2018 Jun;66:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Placenta. 2018. PMID: 29884306 Free PMC article.
-
Association of SUMOylation Pathway Genes With Stroke in a Genome-Wide Association Study in India.Neurology. 2021 Jul 27;97(4):e345-e356. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012258. Epub 2021 May 24. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 34031191 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies Identifies Genetic Risk Factors for Stroke in African Americans.Stroke. 2015 Aug;46(8):2063-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009044. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Stroke. 2015. PMID: 26089329 Free PMC article.
-
Human Validation of Genes Associated With a Murine Atherosclerotic Phenotype.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Jun;36(6):1240-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306958. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27079880 Review.
-
Genetic Risk Factors for Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016 Dec;18(12):124. doi: 10.1007/s11886-016-0804-z. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and stroke: a univariate and multivariate Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 21;15:1366023. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1366023. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39497808 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic risk factors underlying white matter hyperintensities and cortical atrophy.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 4;15(1):9517. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53689-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39496600 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin interaction maps of human arterioles reveal new mechanisms for the genetic regulation of blood pressure.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 14:2024.10.09.617511. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.09.617511. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39463975 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Ischemic stroke and sarcopenia have an asymmetric bidirectional relationship based on a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1427692. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1427692. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39450050 Free PMC article.
-
EDNRA affects susceptibility to large artery atherosclerosis stroke through potential inflammatory pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25173. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76190-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39448657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gudbjartsson DF, et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature. 2007;448:353–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/13/13/30194/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- Z99 AG999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138423/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P02811X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/14/55/30806/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS087541/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- RG/16/4/32218/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P013880/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 GM115428/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CH/12/2/29428/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

