Nucleosomes and DNA methylation shape meiotic DSB frequency in Arabidopsis thaliana transposons and gene regulatory regions
- PMID: 29530928
- PMCID: PMC5880243
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.225599.117
Nucleosomes and DNA methylation shape meiotic DSB frequency in Arabidopsis thaliana transposons and gene regulatory regions
Abstract
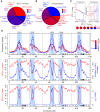
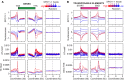
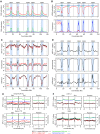
Meiotic recombination initiates from DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) generated by SPO11 topoisomerase-like complexes. Meiotic DSB frequency varies extensively along eukaryotic chromosomes, with hotspots controlled by chromatin and DNA sequence. To map meiotic DSBs throughout a plant genome, we purified and sequenced Arabidopsis thaliana SPO11-1-oligonucleotides. SPO11-1-oligos are elevated in gene promoters, terminators, and introns, which is driven by AT-sequence richness that excludes nucleosomes and allows SPO11-1 access. A positive relationship was observed between SPO11-1-oligos and crossovers genome-wide, although fine-scale correlations were weaker. This may reflect the influence of interhomolog polymorphism on crossover formation, downstream from DSB formation. Although H3K4me3 is enriched in proximity to SPO11-1-oligo hotspots at gene 5' ends, H3K4me3 levels do not correlate with DSBs. Repetitive transposons are thought to be recombination silenced during meiosis, to prevent nonallelic interactions and genome instability. Unexpectedly, we found high SPO11-1-oligo levels in nucleosome-depleted Helitron/Pogo/Tc1/Mariner DNA transposons, whereas retrotransposons were coldspots. High SPO11-1-oligo transposons are enriched within gene regulatory regions and in proximity to immunity genes, suggesting a role as recombination enhancers. As transposon mobility in plant genomes is restricted by DNA methylation, we used the met1 DNA methyltransferase mutant to investigate the role of heterochromatin in SPO11-1-oligo distributions. Epigenetic activation of meiotic DSBs in proximity to centromeres and transposons occurred in met1 mutants, coincident with reduced nucleosome occupancy, gain of transcription, and H3K4me3. Together, our work reveals a complex relationship between chromatin and meiotic DSBs within A. thaliana genes and transposons, with significance for the diversity and evolution of plant genomes.
© 2018 Choi et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic activation of meiotic recombination near Arabidopsis thaliana centromeres via loss of H3K9me2 and non-CG DNA methylation.Genome Res. 2018 Apr;28(4):519-531. doi: 10.1101/gr.227116.117. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 29530927 Free PMC article.
-
Interacting Genomic Landscapes of REC8-Cohesin, Chromatin, and Meiotic Recombination in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2020 Apr;32(4):1218-1239. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00866. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32024691 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation epigenetically silences crossover hot spots and controls chromosomal domains of meiotic recombination in Arabidopsis.Genes Dev. 2015 Oct 15;29(20):2183-202. doi: 10.1101/gad.270876.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26494791 Free PMC article.
-
Hotspots for Initiation of Meiotic Recombination.Front Genet. 2018 Nov 5;9:521. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00521. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30467513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous transposable elements as silencers, enhancers and targets of meiotic recombination.Chromosoma. 2019 Sep;128(3):279-296. doi: 10.1007/s00412-019-00718-4. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Chromosoma. 2019. PMID: 31332531 Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulation of Meiotic Recombination to Hasten Crop Improvement.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;11(3):369. doi: 10.3390/biology11030369. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taming the Turmoil Within: New Insights on the Containment of Transposable Elements.Trends Genet. 2020 Jul;36(7):474-489. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.04.007. Epub 2020 May 27. Trends Genet. 2020. PMID: 32473745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient reduction of DNA methylation at the onset of meiosis in male mice.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Apr 4;11(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0186-0. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 29618374 Free PMC article.
-
LEAFY is a pioneer transcription factor and licenses cell reprogramming to floral fate.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 27;12(1):626. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20883-w. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33504790 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution mapping reveals hotspots and sex-biased recombination in Populus trichocarpa.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Jan 12;13(1):jkac269. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac269. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 36250890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acquaviva L, Székvölgyi L, Dichtl B, Dichtl BS, de La Roche Saint André C, Nicolas A, Géli V. 2013. The COMPASS subunit Spp1 links histone methylation to initiation of meiotic recombination. Science 339: 215–218. - PubMed
-
- Allers T, Lichten M. 2001. Intermediates of yeast meiotic recombination contain heteroduplex DNA. Mol Cell 8: 225–231. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SJ, Caryl AP, Jones GH, Franklin FC. 2002. Asy1, a protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis, localizes to axis-associated chromatin in Arabidopsis and Brassica. J Cell Sci 115: 3645–3655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/K007882/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M004937/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L006847/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/N007557/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
