Mini G protein probes for active G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in live cells
- PMID: 29523687
- PMCID: PMC5949987
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001975
Mini G protein probes for active G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in live cells
Abstract
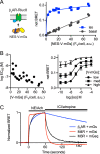
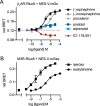
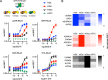
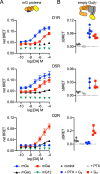
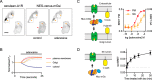
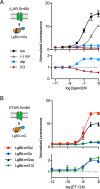
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are key signaling proteins that regulate nearly every aspect of cell function. Studies of GPCRs have benefited greatly from the development of molecular tools to monitor receptor activation and downstream signaling. Here, we show that mini G proteins are robust probes that can be used in a variety of assay formats to report GPCR activity in living cells. Mini G (mG) proteins are engineered GTPase domains of Gα subunits that were developed for structural studies of active-state GPCRs. Confocal imaging revealed that mG proteins fused to fluorescent proteins were located diffusely in the cytoplasm and translocated to sites of receptor activation at the cell surface and at intracellular organelles. Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assays with mG proteins fused to either a fluorescent protein or luciferase reported agonist, superagonist, and inverse agonist activities. Variants of mG proteins (mGs, mGsi, mGsq, and mG12) corresponding to the four families of Gα subunits displayed appropriate coupling to their cognate GPCRs, allowing quantitative profiling of subtype-specific coupling to individual receptors. BRET between luciferase-mG fusion proteins and fluorescent markers indicated the presence of active GPCRs at the plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, and endosomes. Complementation assays with fragments of NanoLuc luciferase fused to GPCRs and mG proteins reported constitutive receptor activity and agonist-induced activation with up to 20-fold increases in luminescence. We conclude that mG proteins are versatile tools for studying GPCR activation and coupling specificity in cells and should be useful for discovering and characterizing G protein subtype-biased ligands.
Keywords: BRET; G protein; G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR); NanoLuc; arrestin; biosensor; mini G protein; molecular pharmacology; protein complementation.
© 2018 Wan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
C. G. T. is a shareholder and member of the scientific advisory board of Heptares Therapeutics
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specific Engineered G Protein Coupling to Histamine Receptors Revealed from Cellular Assay Experiments and Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 17;22(18):10047. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810047. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576210 Free PMC article.
-
A novel luminescence-based β-arrestin recruitment assay for unmodified receptors.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100503. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100503. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33684444 Free PMC article.
-
The luminescent HiBiT peptide enables selective quantitation of G protein-coupled receptor ligand engagement and internalization in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 10;295(15):5124-5135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011952. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32107310 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in assays for GPCR drug discovery.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):C583-C594. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00464.2021. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35816640 Review.
-
Sf9 cells: a versatile model system to investigate the pharmacological properties of G protein-coupled receptors.Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Dec;128(3):387-418. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20705094 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular recognition of an odorant by the murine trace amine-associated receptor TAAR7f.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 30;15(1):7555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51793-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39215004 Free PMC article.
-
Making useful gadgets with miniaturized G proteins.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 11;293(19):7474-7475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H118.002879. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29752421 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1R signaling neighborhoods associate with the susceptibility to adverse drug reactions of incretin mimetics.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 9;14(1):6243. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41893-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37813859 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling, trafficking and glucoregulatory properties of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists exendin-4 and lixisenatide.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;177(17):3905-3923. doi: 10.1111/bph.15134. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32436216 Free PMC article.
-
Microbially conjugated bile salts found in human bile activate the bile salt receptors TGR5 and FXR.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Mar 22;8(4):e0383. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000383. eCollection 2024 Apr 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38517202 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

