Effectiveness of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC): Results of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 29515096
- PMCID: PMC5855927
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.908971
Effectiveness of Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC): Results of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
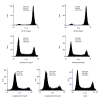
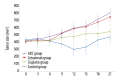
BACKGROUND Human lung cancer is still the leading cause of cancer-related mortality around the world, although a variety of new therapies have been used in the treatment of this disease. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) has revolutionized the field of cancer therapy in recent decades. Unlike traditional chemotherapy that damages the healthy cells, ADC first utilizes monoclonal antibodies to bind tumor-specific antigen targets and then deliver a highly potent cytotoxic agent to kill tumor cells. Thus, ADC can benefit cancer patients because this drug has less severe adverse effects. MATERIAL AND METHODS One type of ADC for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was designed in this study: Erbitux-vc-PAB-MMAE. It is a mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody, Erbitux, conjugating to the tubulin inhibitor auristatin. The efficacy of ADC was investigated through in vitro and in vivo studies. RESULTS Our in vitro study demonstrated that Erbitux-vc-PAB-MMAE could effectively inhibit proliferation of human lung cancer A549 cells, and arrested cell cycle at G2/M phase. In a mouse xenograft model, the results indicated that Erbitux-vc-PAB-MMAE could be exactly delivered to tumor tissues, and effectively inhibited tumor growth via promoting apoptosis of cancer cells. CONCLUSIONS The antibody portion of an ADC drug (Erbitux) was used as a vector to bring the effector molecule (tubulin inhibitor MMAE) to the targeted tumor tissue. This antibody-drug conjugate can exert a strong anti-tumor effect.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monomethyl auristatin E-conjugated anti-EGFR antibody inhibits the growth of human EGFR-positive non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;84(1):61-72. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03848-9. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31037333
-
An antibody-drug conjugate targeting a GSTA glycosite-signature epitope of MUC1 expressed by non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2020 Dec;9(24):9529-9540. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3554. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 33084221 Free PMC article.
-
A glypican-1-targeted antibody-drug conjugate exhibits potent tumor growth inhibition in glypican-1-positive pancreatic cancer and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Neoplasia. 2021 Sep;23(9):939-950. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.07.006. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 34332450 Free PMC article.
-
Pioneering the Way: The Revolutionary Potential of Antibody-Drug Conjugates in NSCLC.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Apr;25(4):556-584. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01196-2. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38520605 Review.
-
Antibody-drug conjugates in advanced lung cancer: Is this a new frontier?Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jun;22(5):217-226. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38805313 Review.
Cited by
-
Glutathione S-Transferase Gene Polymorphisms are Associated with an Improved Treatment Response to Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Meta-Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Oct 20;24:7482-7492. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912373. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30341887 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of the efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates from preclinical to clinical using a semimechanistic PK/PD model: A case study with RC88.Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Jul;16(7):1232-1242. doi: 10.1111/cts.13526. Epub 2023 May 31. Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37259689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng H, Perez-Soler R. Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:e43–e55. - PubMed
-
- Moek KL, de Groot DJA, de Vries EGE, Fehrmann RSN. The antibody-drug conjugate target landscape across a broad range of tumour types. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:3083–91. - PubMed
-
- Willuda J, Linden L, Lerchen HG, et al. Preclinical antitumor efficacy of BAY 1129980-a novel auristatin-based anti-C4.4A (LYPD3) antibody-drug conjugate for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:893–904. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

