Paradigm shift - Metabolic transformation of docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids to bioactives exemplify the promise of fatty acid drug discovery
- PMID: 29499340
- PMCID: PMC5971137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.02.014
Paradigm shift - Metabolic transformation of docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids to bioactives exemplify the promise of fatty acid drug discovery
Abstract
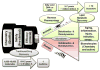
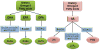
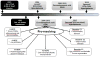
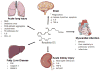
Fatty acid drug discovery (FADD) is defined as the identification of novel, specialized bioactive mediators that are derived from fatty acids and have precise pharmacological/therapeutic potential. A number of reports indicate that dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids and limited intake of omega-6 promotes overall health benefits. In 1929, Burr and Burr indicated the significant role of essential fatty acids for survival and functional health of many organs. In reference to specific dietary benefits of differential omega-3 fatty acids, docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids (DHA and EPA) are transformed to monohydroxy, dihydroxy, trihydroxy, and other complex mediators during infection, injury, and exercise to resolve inflammation. The presented FADD approach describes the metabolic transformation of DHA and EPA in response to injury, infection, and exercise to govern uncontrolled inflammation. Metabolic transformation of DHA and EPA into a number of pro-resolving molecules exemplifies a novel, inexpensive approach compared to traditional, expensive drug discovery. DHA and EPA have been recommended for prevention of cardiovascular disease since 1970. Therefore, the FADD approach is relevant to cardiovascular disease and resolution of inflammation in many injury models. Future research demands identification of novel action targets, receptors for biomolecules, mechanism(s), and drug-interactions with resolvins in order to maintain homeostasis.
Keywords: Inflammation; Lipid mediators; Lipoxygenase; Macrophages; Neutrophils; Omega-3 fatty acids; Resolution; Resolvins.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 106(25):3143–3421. - PubMed
-
- Fish oil supplements. Jama. 312(8):839–840. - PubMed
-
- Akagi D, Chen M, Toy R, Chatterjee A, Conte MS. Systemic delivery of proresolving lipid mediators resolvin D2 and maresin 1 attenuates intimal hyperplasia in mice. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2015;29(6):2504–2513. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

