A novel ligand on astrocytes interacts with natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp44 regulating immune response mediated by NK cells
- PMID: 29447242
- PMCID: PMC5814005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193008
A novel ligand on astrocytes interacts with natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp44 regulating immune response mediated by NK cells
Abstract
NK cells play important role in immunity against pathogens and cancer. NK cell functions are regulated by inhibitory and activating receptors binding corresponding ligands on the surface of target cells. NK cells were shown to be recruited to the CNS following several pathological conditions. NK cells could impact CNS physiology by killing glial cells and by secreting IFN-γ. Astrocytes are intimately involved in immunological and inflammatory events occurring in the CNS and reactive astrogliosis is a key feature in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. There is little data on NK-astrocyte interactions and ligands expressed on astrocytes that could impact NK cell function. Natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs) play a critical role in the cytolytic function of NK cells. Among the NCRs, NKp44 is unique in expression and signal transduction. NKp44 is expressed only upon activation of NK cells and it can mediate both activating and inhibitory signals to NK cells. Here, we have studied the expression and function of natural cytotoxicity receptor NKp44 upon NK-astrocytes interactions in the presence or absence of an HIV peptide (HIV-3S peptide) shown to induce NK cell killing of CD4+ T cells during HIV-infection. Using a fusion protein consisting of the extracellular domain of NKp44 fused to Fc portion of human IgG, we determined the expression of a novel ligand for NKp44 (NKp44L) on astrocytes. Incubation of astrocytes with HIV-3S peptide downregulated NKp44L expression on astrocytes implicating protection from NK mediated killing. Thus, our study showed that NKp44 have a protective effect on astrocytes from NK cell mediated killing during HIV infection and impact astrocyte role in HAND.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

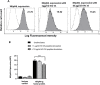
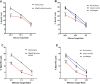
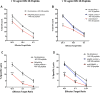
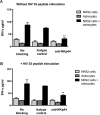
Similar articles
-
NKp44-NKp44 Ligand Interactions in the Regulation of Natural Killer Cells and Other Innate Lymphoid Cells in Humans.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 9;10:719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00719. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cytotoxicity against CD4+ T cells during HIV-1 infection: a gp41 peptide induces the expression of an NKp44 ligand.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 2;102(31):10981-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504315102. Epub 2005 Jul 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16046540 Free PMC article.
-
HIV escape from natural killer cytotoxicity: nef inhibits NKp44L expression on CD4+ T cells.AIDS. 2009 Jun 1;23(9):1077-87. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832cb26b. AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19424050
-
Constitutive expression of ligand for natural killer cell NKp44 receptor (NKp44L) by normal human articular chondrocytes.Cell Immunol. 2013 Sep-Oct;285(1-2):6-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Cell Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24044960
-
Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:197-223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.197. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244035 Review.
Cited by
-
Homer1 promotes the conversion of A1 astrocytes to A2 astrocytes and improves the recovery of transgenic mice after intracerebral hemorrhage.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Mar 14;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02428-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35287697 Free PMC article.
-
The role of natural killer cells in Parkinson's disease.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Sep;52(9):1517-1525. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-00505-7. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32973221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Immunomodulatory Activity of a Selected Strain Bifidobacterium bifidum H3-R2 as Evidenced in vitro and in Immunosuppressed Mice.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 1;11:2089. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02089. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32983062 Free PMC article.
-
NKp44-NKp44 Ligand Interactions in the Regulation of Natural Killer Cells and Other Innate Lymphoid Cells in Humans.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 9;10:719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00719. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Central Nervous System.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 3;13:837250. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837250. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35185929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giulian D. Immune responses and dementia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;835:91–110. . - PubMed
-
- McArthur JC, Haughey N, Gartner S, Conant K, Pardo C, Nath A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia: an evolving disease. J Neurovirol. 2003;9(2):205–21. doi: 10.1080/13550280390194109 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eugenin EA, Clements JE, Zink MC, Berman JW. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of human astrocytes disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity by a gap junction-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci. 2011;31(26):9456–65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1460-11.2011 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3132881. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poli A, Kmiecik J, Domingues O, Hentges F, Blery M, Chekenya M, et al. NK cells in central nervous system disorders. J Immunol. 2013;190(11):5355–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203401 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115526 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

