Preclinical characterization of anlotinib, a highly potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor
- PMID: 29446853
- PMCID: PMC5891194
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13536
Preclinical characterization of anlotinib, a highly potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor
Abstract
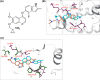
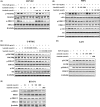
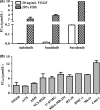
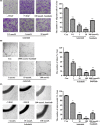
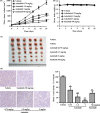
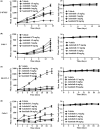
Abrogating tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR2) has been established as a therapeutic strategy for treating cancer. However, because of their low selectivity, most small molecule inhibitors of VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase show unexpected adverse effects and limited anticancer efficacy. In the present study, we detailed the pharmacological properties of anlotinib, a highly potent and selective VEGFR2 inhibitor, in preclinical models. Anlotinib occupied the ATP-binding pocket of VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase and showed high selectivity and inhibitory potency (IC50 <1 nmol/L) for VEGFR2 relative to other tyrosine kinases. Concordant with this activity, anlotinib inhibited VEGF-induced signaling and cell proliferation in HUVEC with picomolar IC50 values. However, micromolar concentrations of anlotinib were required to inhibit tumor cell proliferation directly in vitro. Anlotinib significantly inhibited HUVEC migration and tube formation; it also inhibited microvessel growth from explants of rat aorta in vitro and decreased vascular density in tumor tissue in vivo. Compared with the well-known tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib, once-daily oral dose of anlotinib showed broader and stronger in vivo antitumor efficacy and, in some models, caused tumor regression in nude mice. Collectively, these results indicate that anlotinib is a well-tolerated, orally active VEGFR2 inhibitor that targets angiogenesis in tumor growth, and support ongoing clinical evaluation of anlotinib for a variety of malignancies.
Keywords: VEGF; VEGFR2; angiogenesis; anlotinib; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anlotinib, a novel small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses growth and metastasis via dual blockade of VEGFR2 and MET in osteosarcoma.Int J Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;145(4):979-993. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32180. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30719715
-
Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing the activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ and FGFR1.Gene. 2018 May 15;654:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.026. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29454091
-
Bevacizumab promotes active biological behaviors of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by activating TGFβ1 pathways via off-VEGF signaling.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 May 15;17(2):418-432. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0215. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32587778 Free PMC article.
-
A preclinical review of sunitinib, a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with anti-angiogenic and antitumour activities.Ann Oncol. 2007 Sep;18 Suppl 10:x3-10. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdm408. Ann Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17761721 Review.
-
Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Sep 19;11(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0664-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30231931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bronchopleural fistula in squamous cell lung cancer following anlotinib treatment: A case report.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec;11(6):595-598. doi: 10.3892/mco.2019.1939. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31798876 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Clinical Efficacy of 'Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) and Anlotinib' Than CCRT in Patients with Locally Advanced ESCC.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221080939. doi: 10.1177/15330338221080939. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35235470 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Anlotinib, a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study.J Anal Methods Chem. 2019 Dec 10;2019:5016757. doi: 10.1155/2019/5016757. eCollection 2019. J Anal Methods Chem. 2019. PMID: 31886022 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades for Patients with Previously Treated Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Retrospective Study.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Apr 12;15:3977-3989. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S352536. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35440872 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2018 Jul;78(10):1057-1062. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0939-x. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29943374 Review.
References
-
- Bussolino F, Mantovani A, Persico G. Molecular mechanisms of blood vessel formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:251‐256. - PubMed
-
- Harper J, Moses MA. Molecular regulation of tumor angiogenesis: mechanisms and therapeutic implications In: Bignold LP, ed. Cancer: Cell Structures, Carcinogens and Genomic Instability. Experientia Supplementum, vol. 96, Basel, Switzerland: Birkhäuser; 2006:223‐268. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653‐660. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1757‐1763. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:1‐18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

