Therapeutic Opportunities in Eukaryotic Translation
- PMID: 29440069
- PMCID: PMC5983196
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032995
Therapeutic Opportunities in Eukaryotic Translation
Abstract
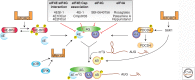
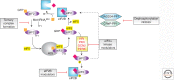
The ability to block biological processes with selective small molecules provides advantages distinct from most other experimental approaches. These include rapid time to onset, swift reversibility, ability to probe activities in manners that cannot be accessed by genetic means, and the potential to be further developed as therapeutic agents. Small molecule inhibitors can also be used to alter expression and activity without affecting the stoichiometry of interacting partners. These tenets have been especially evident in the field of translation. Small molecule inhibitors were instrumental in enabling investigators to capture short-lived complexes and characterize specific steps of protein synthesis. In addition, several drugs that are the mainstay of modern antimicrobial drug therapy are potent inhibitors of prokaryotic translation. Currently, there is much interest in targeting eukaryotic translation as decades of research have revealed that deregulated protein synthesis in cancer cells represents a targetable vulnerability. In addition to being potential therapeutics, small molecules that manipulate translation have also been shown to influence cognitive processes such as memory. In this review, we focus on small molecule modulators that target the eukaryotic translation initiation apparatus and provide an update on their potential application to the treatment of disease.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the translation machinery in cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Apr;14(4):261-78. doi: 10.1038/nrd4505. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25743081 Review.
-
Inhibitors of translation initiation as cancer therapeutics.Future Med Chem. 2009 Dec;1(9):1709-22. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.122. Future Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 21425987 Review.
-
Targeting translation regulators improves cancer therapy.Genomics. 2021 Jan;113(1 Pt 2):1247-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.11.011. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33189778 Review.
-
Small-molecule inhibition of the interaction between the translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIF4G.Cell. 2007 Jan 26;128(2):257-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.046. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17254965
-
Molecular Pathways: The eIF4F Translation Initiation Complex-New Opportunities for Cancer Treatment.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 1;23(1):21-25. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2362. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27789529 Review.
Cited by
-
Reversal of memory and autism-related phenotypes in Tsc2+/- mice via inhibition of Nlgn1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 24;11:1205112. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1205112. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37293130 Free PMC article.
-
A chemical screen for modulators of mRNA translation identifies a distinct mechanism of toxicity for sphingosine kinase inhibitors.PLoS Biol. 2021 May 25;19(5):e3001263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001263. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34033645 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome Profiling: Global Views of Translation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 May 1;11(5):a032698. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032698. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30037969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular delivery of dinucleotides by conjugation with small molecules: targeting translation initiation for anticancer applications.Chem Sci. 2021 Jun 29;12(30):10242-10251. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02143e. eCollection 2021 Aug 4. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34377411 Free PMC article.
-
Novel eIF4A1 inhibitors with anti-tumor activity in lymphoma.Mol Med. 2022 Sep 4;28(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00534-0. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36058921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alain T, Morita M, Fonseca BD, Yanagiya A, Siddiqui N, Bhat M, Zammit D, Marcus V, Metrakos P, Voyer LA, et al. 2012. eIF4E/4E-BP ratio predicts the efficacy of mTOR targeted therapies. Cancer Res 72: 6468–6476. - PubMed
-
- Atkins C, Liu Q, Minthorn E, Zhang SY, Figueroa DJ, Moss K, Stanley TB, Sanders B, Goetz A, Gaul N, et al. 2013. Characterization of a novel PERK kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 73: 1993–2002. - PubMed
-
- Axten JM, Medina JR, Feng Y, Shu A, Romeril SP, Grant SW, Li WH, Heerding DA, Minthorn E, Mencken T, et al. 2012. Discovery of 7-methyl-5-(1-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-5-yl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (GSK2606414), a potent and selective first-in-class inhibitor of protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). J Med Chem 55: 7193–7207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
