A novel miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry contributes to leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 29439669
- PMCID: PMC5811974
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4097-z
A novel miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry contributes to leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneous group of hematopoietic malignancies due to sophisticated genetic mutations and epigenetic dysregulation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a class of small non-coding RNAs, are important regulators of gene expression in all biological processes, including leukemogenesis. Recently, miR-375 has been reported to be a suppressive miRNA in multiple types of cancers, but its underlying anti-leukemia activity in AML is largely unknown.
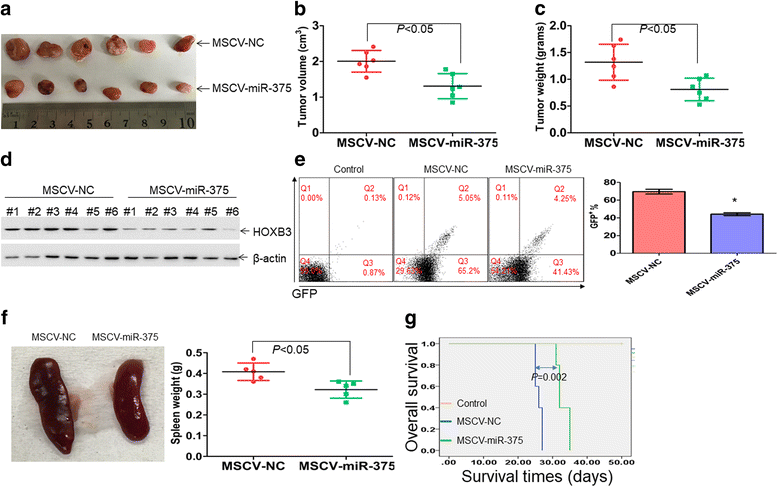
Methods: Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the expression of miR-375 and HOXB3 in leukemic cells and normal controls. Targets of miR-375 were confirmed by western blot and luciferase assay. Phenotypic effects of miR-375 overexpression and HOXB3 knockdown were assessed using viability (trypan blue exclusion assay), colony formation/replating, as well as tumor xenograft assays in vivo.
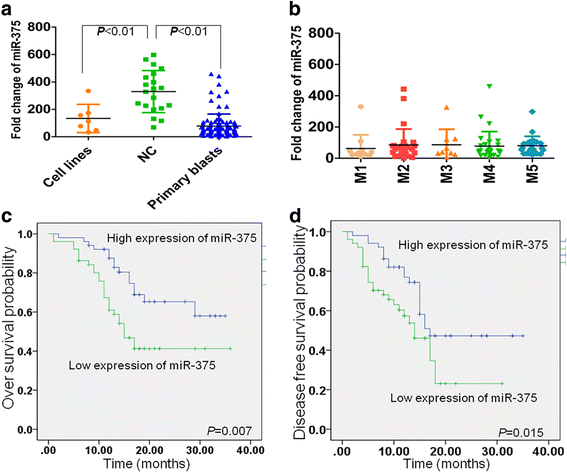
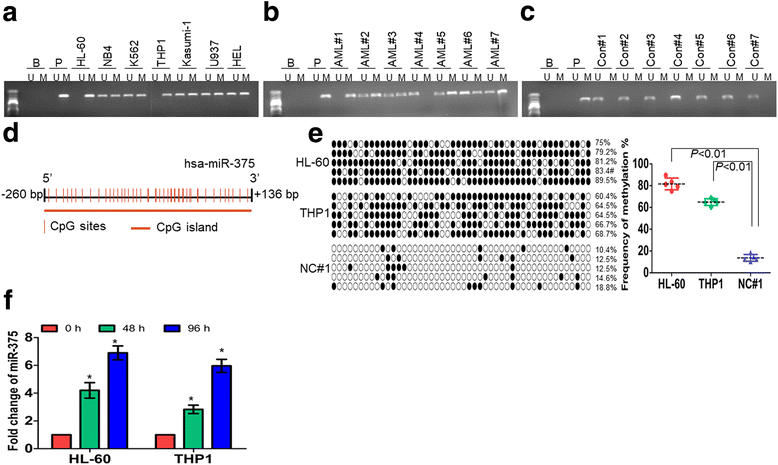
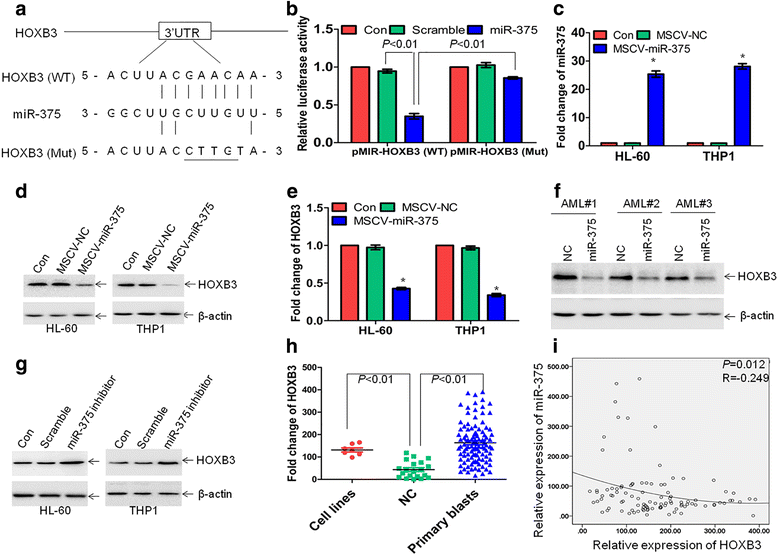
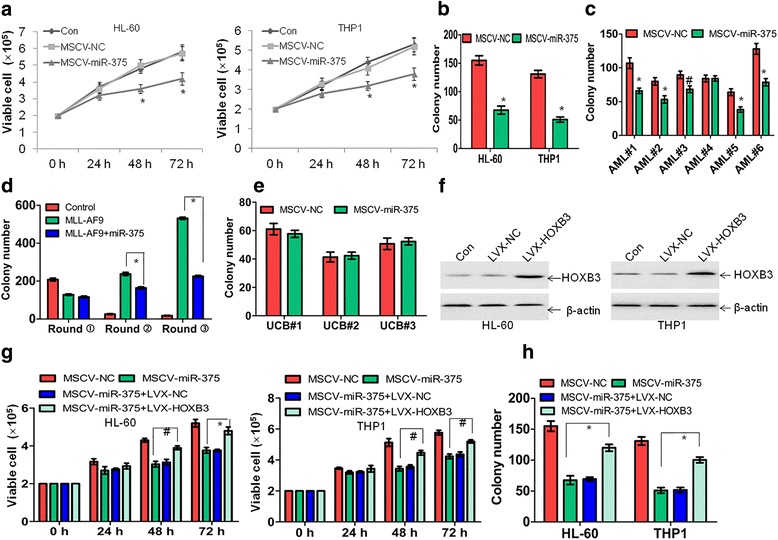
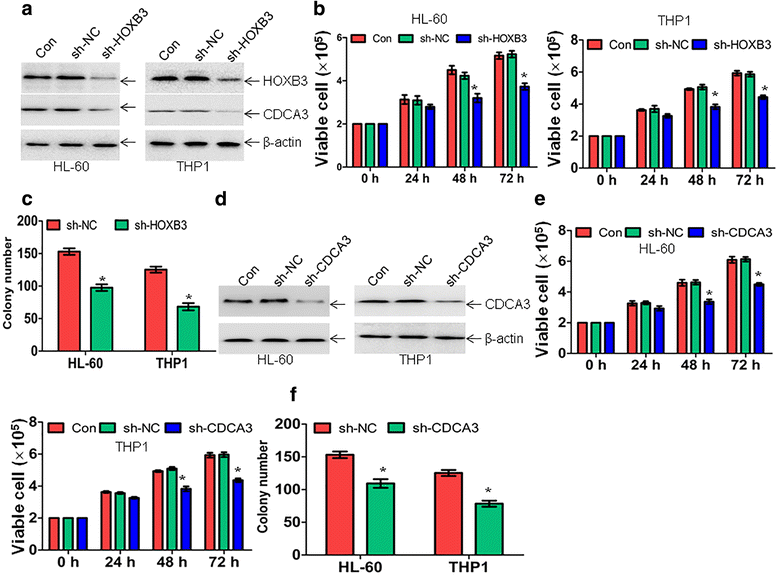
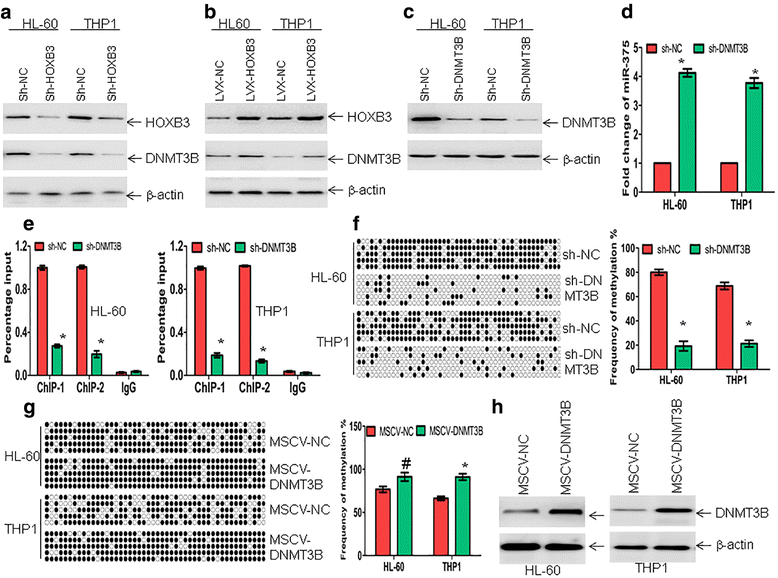
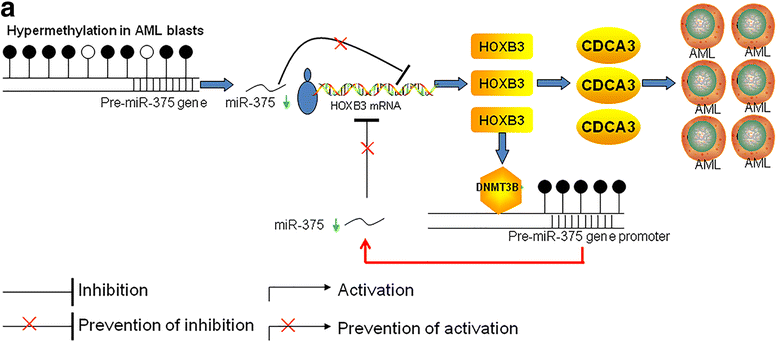
Results: The expression of miR-375 was substantially decreased in leukemic cell lines and primary AML blasts compared with normal controls, because DNA hypermethylation of precursor-miR-375 (pre-miR-375) promoter was discovered in leukemic cells but not in normal controls. Lower expression of miR-375 predicted poor outcome in AML patients. Furthermore, forced expression of miR-375 not only decreased proliferation and colony formation in leukemic cells but also reduced xenograft tumor size and prolonged the survival time in a leukemia xenograft mouse model. Mechanistically, overexpression of miR-375 reduced HOXB3 expression and repressed the activity of a luciferase reporter through binding 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of HOXB3 mRNA. Overexpression of HOXB3 partially blocked miR-375-induced arrest of proliferation and reduction of colony number, suggesting that HOXB3 plays an important role in miR-375-induced anti-leukemia activity. Knockdown of HOXB3 by short hairpin RNAs reduced the expression of cell division cycle associated 3 (CDCA3), which decreased cell proliferation. Furthermore, HOXB3 induced DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) expression to bind in the pre-miR-375 promoter and enhanced DNA hypermethylation of pre-miR-375, leading to the lower expression of miR-375.
Conclusions: Collectively, we have identified a miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry which contributes to leukemogenesis and suggests a therapeutic strategy of restoring miR-375 expression in AML.
Keywords: AML; DNA hypermethylation; DNMT3B; HOXB3; miR-375.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (2012025). All patients signed an informed consent for participation. All animal procedures and care were conducted in accordance with institutional guidelines and in compliance with national and international laws and policies.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-9 plays a role in interleukin-10-mediated expression of E-cadherin in acute myelogenous leukemia cells.Cancer Sci. 2017 Apr;108(4):685-695. doi: 10.1111/cas.13170. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28107581 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1.Blood. 2009 Jun 18;113(25):6411-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-170589. Epub 2009 Feb 11. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19211935 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-9 promotes proliferation of leukemia cells in adult CD34-positive acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype by downregulation of Hes1.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7461-71. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4581-x. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26678889
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MicroRNA21 and the various types of myeloid leukemia.Cancer Gene Ther. 2018 Aug;25(7-8):161-166. doi: 10.1038/s41417-018-0025-2. Epub 2018 May 25. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018. PMID: 29795410 Review.
Cited by
-
The Therapeutic Potential of a Strategy to Prevent Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cell Reprogramming in Older Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 27;24(15):12037. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512037. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of HOXB3 correlates with the development of hormone receptor negative breast cancer.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 20;8:e10421. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10421. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240685 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑1271‑5p inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting ZIC2.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jan;19(1):508-514. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9680. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30483794 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Fallopian Ciliated Cells in the Pathogenesis of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 24;19(9):2512. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092512. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs/DNMT3B axis in human cancers: from pathogenesis to clinical significance.J Transl Med. 2023 Sep 13;21(1):621. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04510-y. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37705098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

