Chemopreventive Effect of Aster glehni on Inflammation-Induced Colorectal Carcinogenesis in Mice
- PMID: 29439531
- PMCID: PMC5852778
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10020202
Chemopreventive Effect of Aster glehni on Inflammation-Induced Colorectal Carcinogenesis in Mice
Abstract
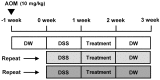
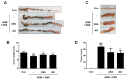
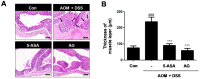
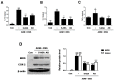
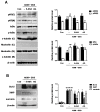
Although Aster glehni is a common dietary herb that has various bioactivities, including anti-diabetic, anti-adipogenic, and anti-inflammatory effects, A. glehni has not been studied in colon cancer. Therefore, we hypothesized the chemopreventive effects of an ethanol extract of A. glehni (AG) on azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS)-induced colitis-associated cancer (CAC) in mice. In this study, we found that treatment with AG significantly attenuated the AOM/DSS-induced enlargement of the spleen and shortening of the colon. In addition, colonic tumor formation, colonic damage, and increased muscle thickness were significantly reduced in AOM/DSS-induced mice fed AG. Treatment with AG also reduced intestinal interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α production and decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 protein expression in mice with AOM/DSS-induced CAC. Furthermore, AG reduced nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation via phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitor of kappa Bα (IκBα), leading to inhibition of NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation. It also downregulated the expression of NF-κB-related proteins, including the B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family and inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), in mice with AOM/DSS-induced CAC. Taken together, these findings suggest that the treatment with AG inhibited colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis in mice, and this chemopreventive effect was strongly mediated by suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway, indicating that AG could be a promising protective agent against CAC.
Keywords: Aster glehni; NF-κB; chemoprevention; colitis-associated cancer; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
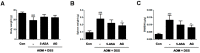
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of an ethanol extract of Aster glehni via inhibition of NF-κB activation in mice with DSS-induced colitis.Food Funct. 2017 Jul 19;8(7):2611-2620. doi: 10.1039/c7fo00369b. Food Funct. 2017. PMID: 28695925
-
Suppression of colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulation of IL-6/STAT3 pathway by balsalazide and VSL#3.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Aug;31(8):1453-61. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13280. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26711554
-
Modified apple polysaccharides suppress the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells induced by lipopolysaccharide.Nutr Res. 2013 Oct;33(10):839-48. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Nutr Res. 2013. PMID: 24074742
-
Chemoprevention of colon cancer by Korean food plant components.Mutat Res. 2003 Feb-Mar;523-524:99-107. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(02)00325-1. Mutat Res. 2003. PMID: 12628507 Review.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory protective effects of yellowtail (Seriola quinqueradiata) milt hydrolysates on human intestinal epithelial cells in vitro and dextran sodium sulphate-induced mouse colitis in vivo.Food Funct. 2022 Sep 22;13(18):9169-9182. doi: 10.1039/d2fo00967f. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 36069409 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Supplementation of Foxtail Millet Ameliorates Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer in Mice via Activation of Gut Receptors and Suppression of the STAT3 Pathway.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 7;12(8):2367. doi: 10.3390/nu12082367. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32784751 Free PMC article.
-
Can Natural Products be Used to Overcome the Limitations of Colorectal Cancer Immunotherapy?Front Oncol. 2022 May 4;12:884423. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.884423. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35600371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Colitis Associated Cancer.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 19;10:585. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00585. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31275360 Free PMC article.
-
Natural CAC chemopreventive agents from Ilex rotunda Thunb.J Nat Med. 2019 Jun;73(3):456-467. doi: 10.1007/s11418-019-01281-z. Epub 2019 Feb 13. J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 30758715
-
Crocin has pharmacological effects against the pathological behavior of colon cancer cells by interacting with the STAT3 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Feb;19(2):1297-1303. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8329. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32010302 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

