MicroRNAs Associated With Reverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Humans Identify Pathways of Heart Failure Progression
- PMID: 29438982
- PMCID: PMC5813824
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004278
MicroRNAs Associated With Reverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Humans Identify Pathways of Heart Failure Progression
Abstract
Background: Plasma extracellular RNAs have recently garnered interest as biomarkers in heart failure (HF). Most studies in HF focus on single extracellular RNAs related to phenotypes and outcomes, and few describe their functional roles. We hypothesized that clusters of plasma microRNAs (miRNAs) associated with left ventricular (LV) remodeling in human HF would identify novel subsets of genes involved in HF in animal models.
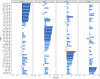
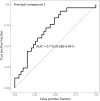
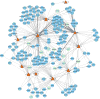
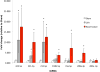
Methods and results: We prospectively measured circulating miRNAs in 64 patients with systolic HF (mean age, 64.8 years; 91% men; median LV ejection fraction, 26%) with serial echocardiography (10 months apart) during medical therapy. We defined LV reverse remodeling as a 15% reduction in LV end-systolic volume index. Using principal components analysis, we identified a component associated with LV reverse remodeling (odds ratio=3.99; P=0.01) that provided risk discrimination for LV reverse remodeling superior to a clinical model (C statistic, 0.58 for a clinical model versus 0.71 for RNA-based model). Using network bioinformatics, we uncovered genes not previously widely described in HF regulated simultaneously by >2 miRNAs. We observed increased myocardial expression of these miRNAs during HF development in animals, with downregulation of target gene expression, suggesting coordinate miRNA-mRNA regulation. Target mRNAs were involved in autophagy, metabolism, and inflammation.
Conclusions: Plasma miRNAs associated with LV reverse remodeling in humans are dysregulated in animal HF and target clusters of genes involved in mechanisms implicated in HF. A translational approach integrating human HF, bioinformatics, and model systems may uncover novel pathways involved in HF.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00351390.
Keywords: RNA, messenger; downregulation; heart failure; microRNAs; myocardium.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

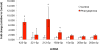
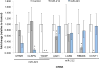
Comment in
-
Plasma MicroRNA Clusters in Human Left Ventricular Remodeling: A Biomarker and Discovery Platform.Circ Heart Fail. 2018 Feb;11(2):e004793. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004793. Circ Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29438983 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Left Ventricular Reverse Remodeling With Biventricular Versus Right Ventricular Pacing in Patients With Atrioventricular Block and Heart Failure in the BLOCK HF Trial.Circ Heart Fail. 2015 May;8(3):510-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001626. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Circ Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 25697851 Clinical Trial.
-
Left Ventricular Architecture, Long-Term Reverse Remodeling, and Clinical Outcome in Mild Heart Failure With Cardiac Resynchronization: Results From the REVERSE Trial.JACC Heart Fail. 2017 Mar;5(3):169-178. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2016.11.012. JACC Heart Fail. 2017. PMID: 28254122
-
Long-term impact of cardiac resynchronization therapy in mild heart failure: 5-year results from the REsynchronization reVErses Remodeling in Systolic left vEntricular dysfunction (REVERSE) study.Eur Heart J. 2013 Sep;34(33):2592-9. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht160. Epub 2013 May 2. Eur Heart J. 2013. PMID: 23641006 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in the development of left ventricular remodeling and postmyocardial infarction heart failure.Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020 Jan 31;130(1):59-65. doi: 10.20452/pamw.15137. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 31933487 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs as Blood-Based Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 5;21(23):9285. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239285. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast activation protein: Pivoting cancer/chemotherapeutic insight towards heart failure.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;219:115914. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115914. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37956895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marked disparity of microRNA modulation by cGMP-selective PDE5 versus PDE9 inhibitors in heart disease.JCI Insight. 2018 Aug 9;3(15):e121739. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121739. eCollection 2018 Aug 9. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30089721 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma microRNAs in human left ventricular reverse remodelling.Open Med (Wars). 2020 Jul 1;15(1):586-588. doi: 10.1515/med-2020-0179. eCollection 2020. Open Med (Wars). 2020. PMID: 33336015 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Circulating microRNA-409-5p and USP7 are associated with left ventricular remodeling in patients with acute myocardial infarction.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Nov 2;24(1):615. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04299-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39488705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boettger T, Braun T. A new level of complexity: the role of microRNAs in cardiovascular development. Circ Res. 2012;110:1000–13. - PubMed
-
- Zampetaki A, Mayr M. MicroRNAs in vascular and metabolic disease. Circ Res. 2012;110:508–22. - PubMed
-
- Naga Prasad SV, Duan ZH, Gupta MK, Surampudi VS, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Kotwal A, Moravec CS, Starling RC, Perez DM, Sen S, Wu Q, Plow EF, Croce CM, Karnik S. Unique microRNA profile in end-stage heart failure indicates alterations in specific cardiovascular signaling networks. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:27487–99. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

