Measuring replication competent HIV-1: advances and challenges in defining the latent reservoir
- PMID: 29433524
- PMCID: PMC5810003
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-018-0404-7
Measuring replication competent HIV-1: advances and challenges in defining the latent reservoir
Abstract
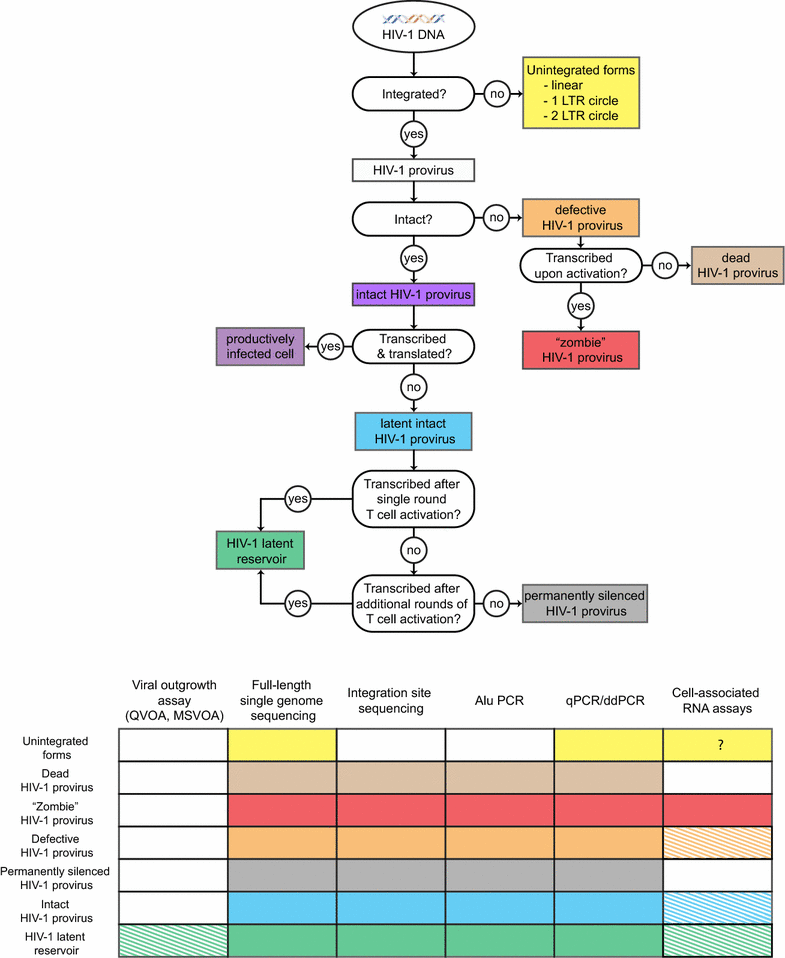
Antiretroviral therapy cannot cure HIV-1 infection due to the persistence of a small number of latently infected cells harboring replication-competent proviruses. Measuring persistent HIV-1 is challenging, as it consists of a mosaic population of defective and intact proviruses that can shift from a state of latency to active HIV-1 transcription. Due to this complexity, most of the current assays detect multiple categories of persistent HIV-1, leading to an overestimate of the true size of the latent reservoir. Here, we review the development of the viral outgrowth assay, the gold-standard quantification of replication-competent proviruses, and discuss the insights provided by full-length HIV-1 genome sequencing methods, which allowed us to unravel the composition of the proviral landscape. In this review, we provide a dissection of what defines HIV-1 persistence and we examine the unmet needs to measure the efficacy of interventions aimed at eliminating the HIV-1 reservoir.
Keywords: HIV-1 persistence; Measuring HIV-1 latent reservoir; Replication-competent HIV-1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequence Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Novel Assays for Intact Proviral HIV-1 DNA.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e01986-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01986-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361426 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring HIV Persistence on Antiretroviral Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1075:265-284. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0484-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030797 Review.
-
Low Inducibility of Latent Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Proviruses as a Major Barrier to Cure.J Infect Dis. 2021 Feb 15;223(12 Suppl 2):13-21. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa649. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33586775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measuring integrated HIV DNA ex vivo and in vitro provides insights about how reservoirs are formed and maintained.Retrovirology. 2018 Feb 17;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12977-018-0396-3. Retrovirology. 2018. PMID: 29452580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paucity of Intact Non-Induced Provirus with Early, Long-Term Antiretroviral Therapy of Perinatal HIV Infection.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 8;12(2):e0170548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170548. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28178277 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
QuickFit: A High-Throughput RT-qPCR-Based Assay to Quantify Viral Growth and Fitness In Vitro.Viruses. 2024 Aug 19;16(8):1320. doi: 10.3390/v16081320. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205294 Free PMC article.
-
A novel high-throughput microwell outgrowth assay for HIV-infected cells.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0179823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01798-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38376258 Free PMC article.
-
HIVepsilon-seq-scalable characterization of intact persistent proviral HIV reservoirs in women.J Virol. 2023 Nov 30;97(11):e0070523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00705-23. Epub 2023 Oct 16. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37843370 Free PMC article.
-
Automated microarray platform for single-cell sorting and collection of lymphocytes following HIV reactivation.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Jun 21;8(5):e10551. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10551. eCollection 2023 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37693052 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting edge strategies for screening of novel anti-HIV drug candidates against HIV infection: A concise overview of cell based assays.Heliyon. 2023 May 5;9(5):e16027. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16027. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37215829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

