Hijacking of the Host Ubiquitin Network by Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 29376029
- PMCID: PMC5770618
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00487
Hijacking of the Host Ubiquitin Network by Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
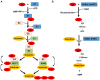
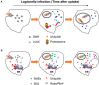
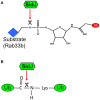
Protein ubiquitination is critical for regulation of numerous eukaryotic cellular processes such as protein homeostasis, cell cycle progression, immune response, DNA repair, and vesicular trafficking. Ubiquitination often leads to the alteration of protein stability, subcellular localization, or interaction with other proteins. Given the importance of ubiquitination in the regulation of host immunity, it is not surprising that many infectious agents have evolved strategies to interfere with the ubiquitination network with sophisticated mechanisms such as functional mimicry. The facultative intracellular pathogen Legionella pneumophila is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease. L. pneumophila is phagocytosed by macrophages and is able to replicate within a niche called Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). The biogenesis of LCV is dependent upon the Dot/Icm type IV secretion system which delivers more than 330 effector proteins into host cytosol. The optimal intracellular replication of L. pneumophila requires the host ubiquitin-proteasome system. Furthermore, membranes of the bacterial phagosome are enriched with ubiquitinated proteins in a way that requires its Dot/Icm type IV secretion system, suggesting the involvement of effectors in the manipulation of the host ubiquitination machinery. Here we summarize recent advances in our understanding of mechanisms exploited by L. pneumophila effector proteins to hijack the host ubiquitination pathway.
Keywords: bacterial virulence; cell signaling; effectors; posttranslational modification; type IV secretion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Divergence of Legionella Effectors Reversing Conventional and Unconventional Ubiquitination.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 21;10:448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00448. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32974222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Polar Legionella Icm/Dot T4SS Establishes Distinct Contact Sites with the Pathogen Vacuole Membrane.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0218021. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02180-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34634944 Free PMC article.
-
The unity of opposites: Strategic interplay between bacterial effectors to regulate cellular homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2021 Dec;297(6):101340. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101340. Epub 2021 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34695417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitination of Sec22b by a novel Legionella pneumophila ubiquitin E3 ligase.mBio. 2023 Dec 19;14(6):e0238223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02382-23. Epub 2023 Oct 26. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37882795 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulation of host vesicular trafficking and innate immune defence by Legionella Dot/Icm effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2011 Dec;13(12):1870-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01710.x. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Cell Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21981078 Review.
Cited by
-
Evasion of phagotrophic predation by protist hosts and innate immunity of metazoan hosts by Legionella pneumophila.Cell Microbiol. 2019 Jan;21(1):e12971. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12971. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30370624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of the Ankyrin H Core Effector of Legionella with the Host LARP7 Component of the 7SK snRNP Complex.mBio. 2019 Aug 27;10(4):e01942-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01942-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31455655 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of Ubiquitin Recognition by a Bacterial Ovarian Tumor Deubiquitinase LotA.J Bacteriol. 2022 Jan 18;204(1):e0037621. doi: 10.1128/JB.00376-21. Epub 2021 Oct 11. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 34633867 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into ubiquitin chain cleavage by Legionella ovarian tumor deubiquitinases.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Apr 26;6(7):e202201876. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201876. Print 2023 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37100438 Free PMC article.
-
Affecting the Effectors: Regulation of Legionella pneumophila Effector Function by Metaeffectors.Pathogens. 2021 Jan 22;10(2):108. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020108. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33499048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-Khodor S., Price C. T., Habyarimana F., Kalia A., Abu Kwaik Y. (2008). A Dot/Icm-translocated ankyrin protein of Legionella pneumophila is required for intracellular proliferation within human macrophages and protozoa. Mol. Microbiol. 70, 908–923. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06453.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

