Nucleolin and ErbB2 inhibition reduces tumorigenicity of ErbB2-positive breast cancer
- PMID: 29352243
- PMCID: PMC5833446
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-017-0067-7
Nucleolin and ErbB2 inhibition reduces tumorigenicity of ErbB2-positive breast cancer
Abstract
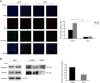
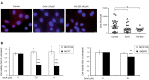
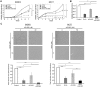
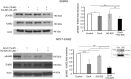
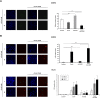
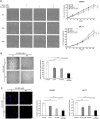
ErbB2, a member of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases, is an essential player in the cell's growth and proliferation signaling pathways. Amplification or overexpression of ErbB2 is observed in ∼30% of breast cancer patients, and often drives cellular transformation and cancer development. Recently, we have shown that ErbB2 interacts with the nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling protein nucleolin, an interaction which enhances cell transformation in vitro, and increases mortality risk and disease progression rate in human breast cancer patients. Given these results, and since acquired resistance to anti-ErbB2-targeted therapy is a major obstacle in treatment of breast cancer, we have examined the therapeutic potential of targeting the ErbB2-nucleolin complex. The effect of the nucleolin-specific inhibitor GroA (AS1411) on ErbB2-positive breast cancer was tested in vivo, in a mouse xenograft model for breast cancer; as well as in vitro, alone and in combination with the ErbB2 kinase-inhibitor tyrphostin AG-825. Here, we show that in vivo treatment of ErbB2-positive breast tumor xenografts with GroA reduces tumor size and leads to decreased ErbB2-mediated signaling. Moreover, we found that co-treatment of breast cancer cell lines with GroA and the ErbB2 kinase-inhibitor tyrphostin AG-825 enhances the anti-cancer effects exerted by GroA alone in terms of cell viability, mortality, migration, and invasiveness. We, therefore, suggest a novel therapeutic approach, consisting of combined inhibition of ErbB2 and nucleolin, which has the potential to improve breast cancer treatment efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nucleolin-binding by ErbB2 enhances tumorigenicity of ErbB2-positive breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65320-65334. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11323. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27542246 Free PMC article.
-
Interfering with the interaction between ErbB1, nucleolin and Ras as a potential treatment for glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 30;5(18):8602-13. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2343. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25261371 Free PMC article.
-
Increased erbB3 promotes erbB2/neu-driven mammary tumor proliferation and co-targeting of erbB2/erbB3 receptors exhibits potent inhibitory effects on breast cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6143-56. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261492 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance to small molecule ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;14(21):6730-4. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0581. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18980964 Review.
-
The ErbB2 signaling network as a target for breast cancer therapy.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006 Jan;11(1):13-25. doi: 10.1007/s10911-006-9009-1. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 16947083 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of MMP2 mRNA by its interaction with miR-20a and Nucleolin in breast cancer cell lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Mar;48(3):2315-2324. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06261-9. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33788053
-
Altered mitochondrial dynamics and function in APOE4-expressing astrocytes.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 24;11(7):578. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02776-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32709881 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleolus, an ally, and an enemy of cancer cells.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Dec;150(6):607-629. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1706-5. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30105457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational Control of RNA-Binding Proteins and Disease-Related Dysregulation.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 27;8:658852. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.658852. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33987205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Non-G-Quadruplex DNA Aptamer Targeting NCL for Diagnosis and Therapy in Bladder Cancer.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Aug;12(20):e2300791. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202300791. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 37262080 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

