Pharmacological activation of PPARγ inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation through a caveolin-1-targeted and -dependent mechanism in PASMCs
- PMID: 29351409
- PMCID: PMC5966784
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00143.2017
Pharmacological activation of PPARγ inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation through a caveolin-1-targeted and -dependent mechanism in PASMCs
Abstract
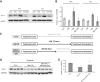
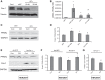
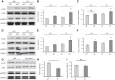
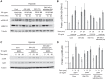
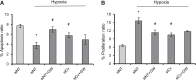
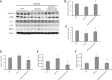
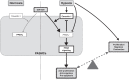
Previously, we and others have demonstrated that activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) by specific pharmacological agonists inhibits the pathogenesis of chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension (CHPH) by suppressing the proliferation and migration in distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Moreover, these beneficial effects of PPARγ are mediated by targeting the intracellular calcium homeostasis and store-operated calcium channel (SOCC) proteins, including the main caveolae component caveolin-1. However, other than the caveolin-1 targeted mechanism, in this study, we further uncovered a caveolin-1 dependent mechanism within the activation of PPARγ by the specific agonist GW1929. First, effective knockdown of caveolin-1 by small-interfering RNA (siRNA) markedly abolished the upregulation of GW1929 on PPARγ expression at both mRNA and protein levels; Then, in HEK293T, which has previously been reported with low endogenous caveolin-1 expression, exogenous expression of caveolin-1 significantly enhanced the upregulation of GW1929 on PPARγ expression compared with nontransfection control. In addition, inhibition of PPARγ by either siRNA or pharmacological inhibitor T0070907 led to increased phosphorylation of cellular mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK1/2 and p38. In parallel, GW1929 dramatically decreased the expression of the proliferative regulators (cyclin D1 and PCNA), whereas it increased the apoptotic factors (p21, p53, and mdm2) in hypoxic PASMCs. Furthermore, these effects of GW1929 could be partially reversed by recovery of the drug treatment. In combination, PPARγ activation by GW1929 reversibly drove the cell toward an antiproliferative and proapoptotic phenotype in a caveolin-1-dependent and -targeted mechanism.
Keywords: caveolin-1; extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; p38; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ-Mediated Inhibition on Hypoxia-Triggered Store-Operated Calcium Entry. A Caveolin-1-Dependent Mechanism.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Dec;53(6):882-92. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0002OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26020612 Free PMC article.
-
Sildenafil inhibits hypoxia-induced transient receptor potential canonical protein expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle via cGMP-PKG-PPARγ axis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Aug;49(2):231-40. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0185OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23526219 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate inhibits hypoxia-induced enhancement of SOCE in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via the PKG-PPAR-γ signaling axis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):C136-49. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00252.2015. Epub 2016 May 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27194472 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-sensing receptor in the development and treatment of pulmonary hypertension.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):975-981. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06065-3. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33394231 Review.
-
PPARγ is a gatekeeper for extracellular matrix and vascular cell homeostasis: beneficial role in pulmonary hypertension and renal/cardiac/pulmonary fibrosis.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020 Mar;29(2):171-179. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000580. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 31815758 Review.
Cited by
-
The pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor reduces development of lung fibrosis and attenuates cardiorespiratory manifestations in a transgenic mouse model of systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Sep 6;23(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02592-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34488870 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced Proliferation by Suppressing Caveolin-1/SOCE/[Ca2+]i Signaling Axis in Human PASMCs.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 8;2021:5551504. doi: 10.1155/2021/5551504. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33928148 Free PMC article.
-
The critical roles of caveolin-1 in lung diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1417834. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1417834. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39380904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ameshima S, Golpon H, Cool CD, Chan D, Vandivier RW, Gardai SJ, Wick M, Nemenoff RA, Geraci MW, Voelkel NF. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) expression is decreased in pulmonary hypertension and affects endothelial cell growth. Circ Res 92: 1162–1169, 2003. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000073585.50092.14. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Baek SJ, Liu S, Safe S. 1,1-Bis(3′-indolyl)-1-(p-substitutedphenyl)methanes are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists but decrease HCT-116 colon cancer cell survival through receptor-independent activation of early growth response-1 and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1. Mol Pharmacol 68: 1782–1792, 2005. doi:10.1124/mol.105.017046. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Safe S. 1,1-bis(3′-indolyl)-1-(p-substitutedphenyl)methanes inhibit growth, induce apoptosis, and decrease the androgen receptor in LNCaP prostate cancer cells through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-independent pathways. Mol Pharmacol 71: 558–569, 2007. doi:10.1124/mol.106.028696. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

