Condition-specific transcriptional regulation of neuronal ion channel genes in brain ischemia
- PMID: 29348796
- PMCID: PMC5770516
Condition-specific transcriptional regulation of neuronal ion channel genes in brain ischemia
Abstract
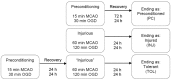
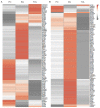
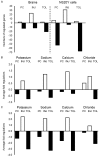
In the context of seeking novel therapeutic targets for treating ischemic stroke, the preconditioning ischemia-induced brain ischemic tolerance has been used as a model of endogenously operative, broad-based neuroprotective mechanisms. Targeting such mechanisms is considered potentially less prone to adverse side effects, as those seen in many failed clinical trials that focus on single targets using exogenous compounds. Results from previous studies have revealed an overall decrease in potassium channel activity in tolerance development. The objective of this study is to identify ion channel genes that are differentially regulated under different brain ischemic conditions, as a mean to identify those ion channels that are associated with ischemic brain injury and ischemic tolerance. In mice in vivo, transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. In cultured neuronal cells in vitro, simulated ischemia was modeled by oxygen-glucose deprivation. For both in vivo and in vitro studies, three principal ischemic conditions were included: ischemic-preconditioned, injured and tolerant, respectively, plus appropriate controls. In these model systems, transcript levels of a panel of 84 neuronal ion channels genes were analyzed with a quantitative real-time PCR mini-array. The results showed that, both in vivo and in vitro, there was a predominant down regulation in neuronal ion channel genes under ischemic-tolerant conditions, and an up regulation in ischemic injury. Similar changes were observed among potassium, sodium and calcium channel genes. A number of regulated genes exhibited opposing changes under ischemic-injured and ischemic-tolerant conditions. This subset of ion channel genes exemplifies potentially novel leads for developing multi-factorial therapeutic targets for treating ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke; ion channels; neuronal excitability; neuroprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TREK-2 Mediates the Neuroprotective Effect of Isoflurane Preconditioning Against Acute Cerebral Ischemia in the Rat.Rejuvenation Res. 2019 Aug;22(4):325-334. doi: 10.1089/rej.2017.2039. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Rejuvenation Res. 2019. PMID: 30412001
-
Genomics of preconditioning.Stroke. 2004 Nov;35(11 Suppl 1):2683-6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000143735.89281.bb. Epub 2004 Sep 30. Stroke. 2004. PMID: 15459430
-
ORAI1/STIM1 Interaction Intervenes in Stroke and in Neuroprotection Induced by Ischemic Preconditioning Through Store-Operated Calcium Entry.Stroke. 2019 May;50(5):1240-1249. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024115. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31009360
-
Non-NMDAR neuronal Ca(2+)-permeable channels in delayed neuronal death and as potential therapeutic targets for ischemic brain damage.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015 Jul;19(7):879-92. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1021781. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25732672 Review.
-
BMS-204352: a potassium channel opener developed for the treatment of stroke.CNS Drug Rev. 2002 Winter;8(4):353-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00233.x. CNS Drug Rev. 2002. PMID: 12481191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium Accumulation in Infected Cells and Ion Transporters Mistargeting in Nodules of Medicago truncatula: Two Ugly Items That Hinder Coping with Salt Stress Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10618. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810618. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142539 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Promotes Differentiation of Ischemia-Activated Adult Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells to Neuronal Precursors.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 25;15:628983. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.628983. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–360. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
