An Integrated View of Immunometabolism
- PMID: 29328913
- PMCID: PMC8451723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.025
An Integrated View of Immunometabolism
Abstract
The worldwide obesity epidemic has emerged as a major cause of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Chronic tissue inflammation is a well-recognized feature of obesity, and the field of immunometabolism has witnessed many advances in recent years. Here, we review the major features of our current understanding with respect to chronic obesity-related inflammation in metabolic tissues and focus on how these inflammatory changes affect insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, food intake, and glucose homeostasis. There is a growing appreciation of the varied and sometimes integrated crosstalk between cells within a tissue (intraorgan) and tissues within an organism (interorgan) that supports inflammation in the context of metabolic dysregulation. Understanding these pathways and modes of communication has implications for translational studies. We also briefly summarize the state of this field with respect to potential current and developing therapeutics.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

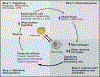
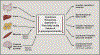
Similar articles
-
[Insulin resistance pathogenesis in metabolic obesity].Biomed Khim. 2015 Jan-Feb;61(1):70-82. doi: 10.18097/pbmc20156101070. Biomed Khim. 2015. PMID: 25762600 Review. Russian.
-
Indirect Effects of Body Mass Index Growth on Glucose Dysregulation via Inflammation: Causal Moderated Mediation Analysis.Obes Facts. 2019;12(3):316-327. doi: 10.1159/000500422. Epub 2019 May 27. Obes Facts. 2019. PMID: 31132775 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic tissue inflammation and metabolic disease.Genes Dev. 2021 Mar 1;35(5-6):307-328. doi: 10.1101/gad.346312.120. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 33649162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foundations of Immunometabolism and Implications for Metabolic Health and Disease.Immunity. 2017 Sep 19;47(3):406-420. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.08.009. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 28930657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate sensors of pathogen and stress: linking inflammation to obesity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug;132(2):287-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.06.022. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23905917 Review.
Cited by
-
GIPR Signaling in Immune Cells Maintains Metabolically Beneficial Type 2 Immune Responses in the White Fat From Obese Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:643144. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.643144. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717200 Free PMC article.
-
GPSM1 impairs metabolic homeostasis by controlling a pro-inflammatory pathway in macrophages.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 25;13(1):7260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34998-9. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36434066 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of liver fibrosis in metabolic syndrome.eGastroenterology. 2023 Jun;1(1):e100015. doi: 10.1136/egastro-2023-100015. eGastroenterology. 2023. PMID: 37946713 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training-attenuated insulin resistance and liver injury in elderly pre-diabetic patients correlates with NLRP3 inflammasome.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1082050. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1082050. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817440 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Network Topology of Biological Aging and Geroscience-Guided Approaches to COVID-19.Front Aging. 2021 Jul;2:695218. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.695218. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Front Aging. 2021. PMID: 35128530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amar J, Chabo C, Waget A, Klopp P, Vachoux C, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Smirnova N, Bergé M, Sulpice T, Lahtinen S, et al. (2011). Intestinal mucosal adherence and translocation of commensal bacteria at the early onset of type 2 diabetes: molecular mechanisms and probiotic treatment. EMBO Mol. Med 3, 559–572. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

