Analysis of DNA modifications in aging research
- PMID: 29327208
- PMCID: PMC5832665
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-018-0005-3
Analysis of DNA modifications in aging research
Abstract
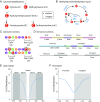
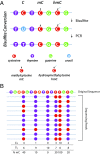
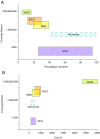
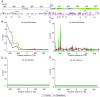
As geroscience research extends into the role of epigenetics in aging and age-related disease, researchers are being confronted with unfamiliar molecular techniques and data analysis methods that can be difficult to integrate into their work. In this review, we focus on the analysis of DNA modifications, namely cytosine methylation and hydroxymethylation, through next-generation sequencing methods. While older techniques for modification analysis performed relative quantitation across regions of the genome or examined average genome levels, these analyses lack the desired specificity, rigor, and genomic coverage to firmly establish the nature of genomic methylation patterns and their response to aging. With recent methodological advances, such as whole genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), bisulfite oligonucleotide capture sequencing (BOCS), and bisulfite amplicon sequencing (BSAS), cytosine modifications can now be readily analyzed with base-specific, absolute quantitation at both cytosine-guanine dinucleotide (CG) and non-CG sites throughout the genome or within specific regions of interest by next-generation sequencing. Additional advances, such as oxidative bisulfite conversion to differentiate methylation from hydroxymethylation and analysis of limited input/single-cells, have great promise for continuing to expand epigenomic capabilities. This review provides a background on DNA modifications, the current state-of-the-art for sequencing methods, bioinformatics tools for converting these large data sets into biological insights, and perspectives on future directions for the field.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Epigenetics; Methods.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing Protocol for the Analysis of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Patterns at Single-Nucleotide Resolution.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2842:353-382. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4051-7_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39012605
-
DNA Methylation Analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1894:181-227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8916-4_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30547463
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of DNA Methylation Through Bisulfite Sequencing Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2198:441-450. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0876-0_32. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32822049
-
Studying the epigenome using next generation sequencing.J Med Genet. 2011 Nov;48(11):721-30. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100242. Epub 2011 Aug 8. J Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 21825079 Review.
-
DNA methylation methods: Global DNA methylation and methylomic analyses.Methods. 2021 Mar;187:28-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Methods. 2021. PMID: 33039572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tamoxifen induction of Cre recombinase does not cause long-lasting or sexually divergent responses in the CNS epigenome or transcriptome: implications for the design of aging studies.Geroscience. 2019 Oct;41(5):691-708. doi: 10.1007/s11357-019-00090-2. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Geroscience. 2019. PMID: 31493147 Free PMC article.
-
Fusogenic liposomes effectively deliver resveratrol to the cerebral microcirculation and improve endothelium-dependent neurovascular coupling responses in aged mice.Geroscience. 2019 Dec;41(6):711-725. doi: 10.1007/s11357-019-00102-1. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Geroscience. 2019. PMID: 31654270 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to environmental enrichment attenuates addiction-like behavior and alters molecular effects of heroin self-administration in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Sep 1;139:26-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.037. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29964093 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-Associated Protein Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Is Correlated With Immune Infiltration in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pan-Cancer Analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 2;7:573619. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.573619. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33240929 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) treatment attenuates oxidative stress and rescues angiogenic capacity in aged cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells: a potential mechanism for the prevention of vascular cognitive impairment.Geroscience. 2019 Oct;41(5):619-630. doi: 10.1007/s11357-019-00074-2. Epub 2019 May 29. Geroscience. 2019. PMID: 31144244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

