Diversity and Connectivity of Layer 5 Somatostatin-Expressing Interneurons in the Mouse Barrel Cortex
- PMID: 29326172
- PMCID: PMC5815450
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2415-17.2017
Diversity and Connectivity of Layer 5 Somatostatin-Expressing Interneurons in the Mouse Barrel Cortex
Abstract
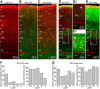
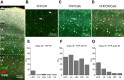
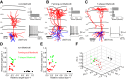
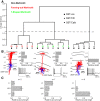
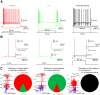
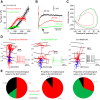
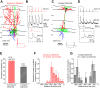
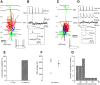
Inhibitory interneurons represent 10-15% of the neurons in the somatosensory cortex, and their activity powerfully shapes sensory processing. Three major groups of GABAergic interneurons have been defined according to developmental, molecular, morphological, electrophysiological, and synaptic features. Dendritic-targeting somatostatin-expressing interneurons (SST-INs) have been shown to display diverse morphological, electrophysiological, and molecular properties and activity patterns in vivo However, the correlation between these properties and SST-IN subtype is unclear. In this study, we aimed to correlate the morphological diversity of layer 5 (L5) SST-INs with their electrophysiological and molecular diversity in mice of either sex. Our morphological analysis demonstrated the existence of three subtypes of L5 SST-INs with distinct electrophysiological properties: T-shaped Martinotti cells innervate L1, and are low-threshold spiking; fanning-out Martinotti cells innervate L2/3 and the lower half of L1, and show adapting firing patterns; non-Martinotti cells innervate L4, and show a quasi-fast spiking firing pattern. We estimated the proportion of each subtype in L5 and found that T-shaped Martinotti, fanning-out Martinotti, and Non-Martinotti cells represent ∼10, ∼50, and ∼40% of L5 SST-INs, respectively. Last, we examined the connectivity between the three SST-IN subtypes and L5 pyramidal cells (PCs). We found that L5 T-shaped Martinotti cells inhibit the L1 apical tuft of nearby PCs; L5 fanning-out Martinotti cells also inhibit nearby PCs but they target the dendrite mainly in L2/3. On the other hand, non-Martinotti cells inhibit the dendrites of L4 neurons while avoiding L5 PCs. Our data suggest that morphologically distinct SST-INs gate different excitatory inputs in the barrel cortex.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Morphologically diverse layer 5 SST-INs show different patterns of activity in behaving animals. However, little is known about the abundance and connectivity of each morphological type and the correlation between morphological subtype and spiking properties. We demonstrate a correlation between the morphological and electrophysiological diversity of layer 5 SST-INs. Based on these findings we built a classifier to infer the abundance of each morphological subtype. Last, using paired recordings combined with morphological analysis, we investigated the connectivity of each morphological subtype. Our data suggest that, by targeting different cell types and cellular compartments, morphologically diverse SST-INs might gate different excitatory inputs in the mouse barrel cortex.
Keywords: barrel cortex; cortical circuits; inhibition; interneurons; somatostatin.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/381622-12$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological Signature and Target Specificity of Inhibitory Circuits Formed by Martinotti Cells in the Mouse Barrel Cortex.J Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;43(1):14-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1661-21.2022. Epub 2022 Nov 16. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36384682 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the morphology of somatostatin-expressing interneurons and their synaptic innervation pattern in the barrel cortex of the GFP-expressing inhibitory neurons mouse.J Comp Neurol. 2020 Feb 1;528(2):244-260. doi: 10.1002/cne.24756. Epub 2019 Aug 24. J Comp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31407339
-
Four Unique Interneuron Populations Reside in Neocortical Layer 1.J Neurosci. 2019 Jan 2;39(1):125-139. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1613-18.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30413647 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory interneurons and their circuit motifs in the many layers of the barrel cortex.Neuroscience. 2018 Jan 1;368:132-151. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.027. Epub 2017 May 18. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 28528964 Review.
-
Diversity and Function of Somatostatin-Expressing Interneurons in the Cerebral Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 17;20(12):2952. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122952. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Burst-dependent synaptic plasticity can coordinate learning in hierarchical circuits.Nat Neurosci. 2021 Jul;24(7):1010-1019. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00857-x. Epub 2021 May 13. Nat Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33986551
-
Synaptic zinc potentiates AMPA receptor function in mouse auditory cortex.Cell Rep. 2023 Aug 29;42(8):112932. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112932. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37585291 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency-dependent gating of feedforward inhibition in thalamofrontal synapses.Mol Brain. 2020 May 6;13(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00608-2. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 32375833 Free PMC article.
-
3D Ultrastructure of Synaptic Inputs to Distinct GABAergic Neurons in the Mouse Primary Visual Cortex.Cereb Cortex. 2021 Mar 31;31(5):2610-2624. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa378. Cereb Cortex. 2021. PMID: 33350443 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol reduces the activity of somatostatin interneurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex: A neural basis for its disinhibitory effect?Neuropharmacology. 2021 May 1;188:108501. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108501. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33636191 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
