Intermittent metabolic switching, neuroplasticity and brain health
- PMID: 29321682
- PMCID: PMC5913738
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn.2017.156
Intermittent metabolic switching, neuroplasticity and brain health
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Intermittent metabolic switching, neuroplasticity and brain health.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Aug;21(8):445. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0342-y. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32606453
Abstract
During evolution, individuals whose brains and bodies functioned well in a fasted state were successful in acquiring food, enabling their survival and reproduction. With fasting and extended exercise, liver glycogen stores are depleted and ketones are produced from adipose-cell-derived fatty acids. This metabolic switch in cellular fuel source is accompanied by cellular and molecular adaptations of neural networks in the brain that enhance their functionality and bolster their resistance to stress, injury and disease. Here, we consider how intermittent metabolic switching, repeating cycles of a metabolic challenge that induces ketosis (fasting and/or exercise) followed by a recovery period (eating, resting and sleeping), may optimize brain function and resilience throughout the lifespan, with a focus on the neuronal circuits involved in cognition and mood. Such metabolic switching impacts multiple signalling pathways that promote neuroplasticity and resistance of the brain to injury and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
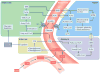
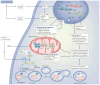
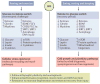
Similar articles
-
Adaptive responses of neuronal mitochondria to bioenergetic challenges: Roles in neuroplasticity and disease resistance.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jan;102:203-216. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.045. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 27908782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise, energy intake, glucose homeostasis, and the brain.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 12;34(46):15139-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2814-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25392482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018 Feb;26(2):254-268. doi: 10.1002/oby.22065. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018. PMID: 29086496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifelong brain health is a lifelong challenge: from evolutionary principles to empirical evidence.Ageing Res Rev. 2015 Mar;20:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Ageing Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25576651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasting for 20 h does not affect exercise-induced increases in circulating BDNF in humans.J Physiol. 2023 Jun;601(11):2121-2137. doi: 10.1113/JP283582. Epub 2023 Jan 11. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36631068
Cited by
-
Effect of Systemic Inflammation on Rat Attentional Function and Neuroinflammation: Possible Protective Role for Food Restriction.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Oct 25;11:296. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00296. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31708767 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria in the signaling pathways that control longevity and health span.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Sep;54:100940. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100940. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31415807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermittent fasting increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Brain Behav. 2020 Jan;10(1):e01444. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1444. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 31804775 Free PMC article.
-
NAD+ in Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Cell Metab. 2019 Oct 1;30(4):630-655. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.001. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 31577933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT3 mediates hippocampal synaptic adaptations to intermittent fasting and ameliorates deficits in APP mutant mice.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 23;10(1):1886. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09897-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31015456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bramble DM, Lieberman DE. Endurance running and the evolution of Homo. Nature. 2004;432:345–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

