The Amino Terminus of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Glycoprotein K (gK) Is Required for gB Binding to Akt, Release of Intracellular Calcium, and Fusion of the Viral Envelope with Plasma Membranes
- PMID: 29321326
- PMCID: PMC5827371
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01842-17
The Amino Terminus of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Glycoprotein K (gK) Is Required for gB Binding to Akt, Release of Intracellular Calcium, and Fusion of the Viral Envelope with Plasma Membranes
Abstract
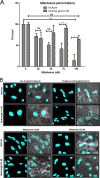
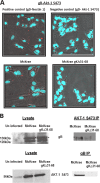
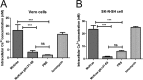
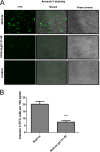
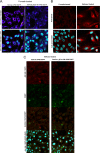
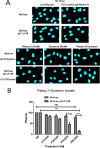
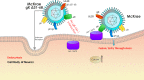
Previously, we have shown that the amino terminus of glycoprotein K (gK) binds to the amino terminus of gB and that deletion of the amino-terminal 38 amino acids of gK prevents herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection of mouse trigeminal ganglia after ocular infection and virus entry into neuronal axons. Recently, it has been shown that gB binds to Akt during virus entry and induces Akt phosphorylation and intracellular calcium release. Proximity ligation and two-way immunoprecipitation assays using monoclonal antibodies against gB and Akt-1 phosphorylated at S473 [Akt-1(S473)] confirmed that HSV-1(McKrae) gB interacted with Akt-1(S473) during virus entry into human neuroblastoma (SK-N-SH) cells and induced the release of intracellular calcium. In contrast, the gB specified by HSV-1(McKrae) gKΔ31-68, lacking the amino-terminal 38 amino acids of gK, failed to interact with Akt-1(S473) and induce intracellular calcium release. The Akt inhibitor miltefosine inhibited the entry of McKrae but not the gKΔ31-68 mutant into SK-N-SH cells. Importantly, the entry of the gKΔ31-68 mutant but not McKrae into SK-N-SH cells treated with the endocytosis inhibitors pitstop-2 and dynasore hydrate was significantly inhibited, indicating that McKrae gKΔ31-68 entered via endocytosis. These results suggest that the amino terminus of gK functions to regulate the fusion of the viral envelope with cellular plasma membranes.IMPORTANCE HSV-1 glycoprotein B (gB) functions in the fusion of the viral envelope with cellular membranes during virus entry. Herein, we show that a deletion in the amino terminus of glycoprotein K (gK) inhibits gB binding to Akt-1(S473), the release of intracellular calcium, and virus entry via fusion of the viral envelope with cellular plasma membranes.
Keywords: Akt; HSV-1; calcium signaling; fusion; glycoprotein B (gB); glycoprotein K (gK).
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The amino terminus of herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein K is required for virion entry via the paired immunoglobulin-like type-2 receptor alpha.J Virol. 2013 Mar;87(6):3305-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02982-12. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23302878 Free PMC article.
-
The amino terminus of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein K (gK) modulates gB-mediated virus-induced cell fusion and virion egress.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(23):12301-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01329-09. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19793812 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of a Predicted β-Sheet Domain within the Amino Terminus of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein K Conserved among Alphaherpesviruses Prevents Virus Entry into Neuronal Axons.J Virol. 2015 Dec 9;90(5):2230-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02468-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26656706 Free PMC article.
-
Two Sides to Every Story: Herpes Simplex Type-1 Viral Glycoproteins gB, gD, gH/gL, gK, and Cellular Receptors Function as Key Players in Membrane Fusion.Viruses. 2021 Sep 16;13(9):1849. doi: 10.3390/v13091849. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus Membrane Fusion.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017;223:29-47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53168-7_2. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28528438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nectin-1 and Non-muscle Myosin Heavy Chain-IIB: Major Mediators of Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry Into Corneal Nerves.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 28;13:830699. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.830699. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35295302 Free PMC article.
-
Go go gadget glycoprotein!: HSV-1 draws on its sizeable glycoprotein tool kit to customize its diverse entry routes.PLoS Pathog. 2019 May 9;15(5):e1007660. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007660. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31071197 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The herpes simplex virus 1 Us3 kinase is involved in assembly of membranes needed for viral envelopment and in distribution of glycoprotein K.F1000Res. 2019 May 23;8:727. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.19194.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31448105 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Requirements for gE, gI, and UL16 among Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Syncytial Variants Suggest Unique Modes of Dysregulating the Mechanism of Cell-to-Cell Spread.J Virol. 2019 Jul 17;93(15):e00494-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00494-19. Print 2019 Aug 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31092572 Free PMC article.
-
Intramuscular Vaccination With the HSV-1(VC2) Live-Attenuated Vaccine Strain Confers Protection Against Viral Ocular Immunopathogenesis Associated With γδT Cell Intracorneal Infiltration.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 15;12:789454. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.789454. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34868077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM. 2001. Herpes simplex viruses and their replication, p 2399–2459. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Chanock RM, Melnick JL, Monath TP, Roizman B, Straus SE (ed), Fields virology, 3rd ed, vol 2 Lippincott-Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Aggarwal A, Miranda-Saksena M, Boadle RA, Kelly BJ, Diefenbach RJ, Alam W, Cunningham AL. 2012. Ultrastructural visualization of individual tegument protein dissociation during entry of herpes simplex virus 1 into human and rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Virol 86:6123–6137. doi:10.1128/JVI.07016-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lycke E, Hamark B, Johansson M, Krotochwil A, Lycke J, Svennerholm B. 1988. Herpes simplex virus infection of the human sensory neuron. An electron microscopy study. Arch Virol 101:87–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

