Quercetin suppresses DNA double-strand break repair and enhances the radiosensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells via p53-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway
- PMID: 29317830
- PMCID: PMC5743179
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S147316
Quercetin suppresses DNA double-strand break repair and enhances the radiosensitivity of human ovarian cancer cells via p53-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway
Abstract
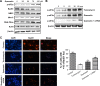
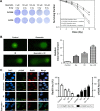
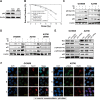
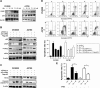
Quercetin is proven to have anticancer effects for many cancers. However, the role of tumor suppressor p53 on quercetin's radiosensitization and regulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response in this process remains obscure. Here, quercetin exposure resulted in ER stress, prolonged DNA repair, and the expression of p53 protein; phosphorylation on serine 15 and 20 increased in combination with X-irradiation. Quercetin pretreatment could potentiate radiation-induced cell death. The combination of irradiation and quercetin treatment aggravated DNA damages and caused typical apoptotic cell death; as well the expression of Bax and p21 elevated and the expression of Bcl-2 decreased. Knocking down of p53 could reverse all the above effects under quercetin in combination with radiation. In addition, quercetin-induced radiosensitization was through stimulation of ATM phosphorylation. In human ovarian cancer xenograft model, combined treatment of quercetin and radiation significantly restrained the growth of tumors, accompanied with the activation of p53, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein, and γ-H2AX. Overall, these results indicated that quercetin acted as a promising radiosensitizer through p53-dependent ER stress signals.
Keywords: ATM kinase; DNA double-strand breaks; eIF-2α (eukaryotic initiation factor 2α); endoplasmic reticulum stress; p53; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acriflavine enhances radiosensitivity of colon cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;44(8):1214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.04.022. Epub 2012 May 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22564437
-
The isoflavonoids genistein and quercetin activate different stress signaling pathways as shown by analysis of site-specific phosphorylation of ATM, p53 and histone H2AX.DNA Repair (Amst). 2004 Mar 4;3(3):235-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.10.014. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004. PMID: 15177039
-
Relationship between DNA double-strand break rejoining and cell survival after exposure to ionizing radiation in human fibroblast strains with differing ATM/p53 status: implications for evaluation of clinical radiosensitivity.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Dec 1;66(5):1498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.064. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 17126209
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic Mechanisms of Quercetin in Liver Cancer: Recent Trends and Advancements.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 20;15(2):712. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020712. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36840034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antitumor effects and molecular mechanisms of action of natural products in ovarian cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):141. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12001. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32934709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 in Colorectal Cancer Promotes Radioresistance and Aggressive Malignance.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Nov 28;15:8365-8380. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S393270. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 36465270 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Preclinical Outcomes of Combining Targeted Therapy With Radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 18;11:749496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.749496. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34733787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-Derived Natural Products in Cancer Research: Extraction, Mechanism of Action, and Drug Formulation.Molecules. 2020 Nov 14;25(22):5319. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225319. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33202681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Involvement of Natural Polyphenols in Molecular Mechanisms Inducing Apoptosis in Tumor Cells: A Promising Adjuvant in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1680. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021680. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Okayasu R. Repair of DNA damage induced by accelerated heavy ions–a mini review. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(5):991–1000. - PubMed
-
- Ye R, Goodarzi AA, Kurz EU, et al. The isoflavonoids genistein and quercetin activate different stress signaling pathways as shown by analysis of site-specific phosphorylation of ATM, p53 and histone H2AX. DNA Rep. 2004;3(3):235–244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

