Toll-Like Receptor 4 Mediates Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation through Caspase-11 Signaling Pathway in Astrocytes
- PMID: 29311802
- PMCID: PMC5733023
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00409
Toll-Like Receptor 4 Mediates Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation through Caspase-11 Signaling Pathway in Astrocytes
Abstract
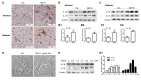
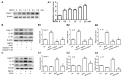
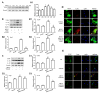
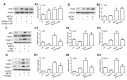
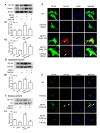
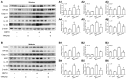
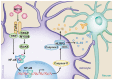
Methamphetamine (METH) is an amphetamine-typed stimulant drug that is increasingly being abused worldwide. Previous studies have shown that METH toxicity is systemic, especially targeting dopaminergic neurons in the central nervous system (CNS). However, the role of neuroinflammation in METH neurotoxicity remains unclear. We hypothesized that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and Caspase-11 are involved in METH-induced astrocyte-related neuroinflammation. We tested our hypothesis by examining the changes of TLR4 and Caspase-11 protein expression in primary cultured C57BL/6 mouse astrocytes and in the midbrain and striatum of mice exposed to METH with western blot and double immunofluorescence labeling. We also determined the effects of blocking Caspase-11 expression with wedelolactone (a specific inhibitor of Caspase-11) or siRNA on METH-induced neuroinflammation in astrocytes. Furthermore, we determined the effects of blocking TLR4 expression with TAK-242 (a specific inhibitor of TLR4) or siRNA on METH-induced neuroinflammation in astrocytes. METH exposure increased Caspase-11 and TLR4 expression both in vitro and in vivo, with the effects in vitro being dose-dependent. Inhibition of Caspase-11 expression with either wedelolactone or siRNAs reduced the expression of inflammasome NLRP3 and pro-inflammatory cytokines. In addition, blocking TLR4 expression inhibited METH-induced activation of NF-κB and Caspase-11 in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that TLR4-Caspase-11 pathway is involved in METH-induced neuroinflammation. These results indicate that Caspase-11 and TLR4 play an important role in METH-induced neuroinflammation and may be potential gene targets for therapeutics in METH-caused neurotoxicity.
Keywords: Caspase-11; Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); astrocyte; inflammasome; methamphetamine; neuroinflammation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Caspase-11 plays an essential role in methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neuron apoptosis.Toxicol Sci. 2015 May;145(1):68-79. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv014. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25631491 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CXCR1 and Interleukin-8 in Methamphetamine-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Aug 3;12:230. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00230. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30123110 Free PMC article.
-
Asiatic acid attenuates methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity through blocking of NF-kB/STAT3/ERK and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Dec 11;14(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1009-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29228978 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation.Ageing Res Rev. 2017 Jul;36:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Ageing Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28235660 Review.
-
The Crosstalk Between Neurons and Glia in Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation.Neurochem Res. 2022 Apr;47(4):872-884. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03513-9. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 34982394 Review.
Cited by
-
Cognitive impairment and changes of red blood cell components and serum levels of IL-6, IL-18, and L-tryptophan in methamphetamine abusers.Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2023 Feb 25;12(1):1-15. eCollection 2023. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2023. PMID: 36937109 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine induces thoracic aortic aneurysm/dissection through C/EBPβ.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Sep 1;1868(9):166447. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166447. Epub 2022 May 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 35643386 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of brain organoids in neurodevelopment and neurological diseases.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Apr 22;28(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00728-4. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 33888112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Microglia in Psychostimulant Addiction.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(2):235-259. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666221208142151. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36503452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MG53 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway in vitro and in vivo.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Dec 20;95:109684. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109684. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31260721 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

