Effects of Strain and Species on the Septo-Temporal Distribution of Adult Neurogenesis in Rodents
- PMID: 29311796
- PMCID: PMC5742116
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00719
Effects of Strain and Species on the Septo-Temporal Distribution of Adult Neurogenesis in Rodents
Abstract
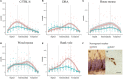
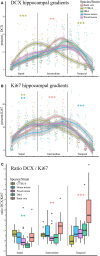
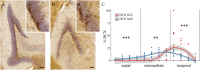
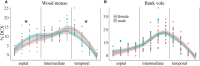
The functional septo-temporal (dorso-ventral) differentiation of the hippocampus is accompanied by gradients of adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) in laboratory rodents. An extensive septal AHN in laboratory mice suggests an emphasis on a relation of AHN to tasks that also depend on the septal hippocampus. Domestication experiments indicate that AHN dynamics along the longitudinal axis are subject to selective pressure, questioning if the septal emphasis of AHN in laboratory mice is a rule applying to rodents in general. In this study, we used C57BL/6 and DBA2/Crl mice, wild-derived F1 house mice and wild-captured wood mice and bank voles to look for evidence of strain and species specific septo-temporal differences in AHN. We confirmed the septal > temporal gradient in C57BL/6 mice, but in the wild species, AHN was low septally and high temporally. Emphasis on the temporal hippocampus was particularly strong for doublecortin positive (DCX+) young neurons and more pronounced in bank voles than in wood mice. The temporal shift was stronger in female wood mice than in males, while we did not see sex differences in bank voles. AHN was overall low in DBA and F1 house mice, but they exhibited the same inversed gradient as wood mice and bank voles. DCX+ young neurons were usually confined to the subgranular zone and deep granule cell layer. This pattern was seen in all animals in the septal and intermediate dentate gyrus. In bank voles and wood mice however, the majority of temporal DCX+ cells were radially dispersed throughout the granule cell layer. Some but not all of the septo-temporal differences were accompanied by changes in the DCX+/Ki67+ cell ratios, suggesting that new neuron numbers can be regulated by both proliferation or the time course of maturation and survival of young neurons. Some of the septo-temporal differences we observe have also been found in laboratory rodents after the experimental manipulation of the molecular mechanisms that control AHN. Adaptations of AHN under natural conditions may operate on these or similar mechanisms, adjusting neurogenesis to the requirements of hippocampal function.
Keywords: Apodemus sylvaticus; Ki67; Mus domesticus; Myodes glareolus; doublecortin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consistent within-group covariance of septal and temporal hippocampal neurogenesis with behavioral phenotypes for exploration and memory retention across wild and laboratory small rodents.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Oct 17;372:112034. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112034. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31201873
-
Habitat-specific shaping of proliferation and neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of wild rodents.Front Neurosci. 2013 Apr 18;7:59. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00059. eCollection 2013. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23616743 Free PMC article.
-
Septo-temporal distribution and lineage progression of hippocampal neurogenesis in a primate (Callithrix jacchus) in comparison to mice.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Jun 29;9:85. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00085. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 26175670 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of progenitor cell/immature neuron markers does not present definitive evidence for adult neurogenesis.Mol Brain. 2019 Dec 10;12(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0522-8. Mol Brain. 2019. PMID: 31823803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult neurogenesis in the primate hippocampus.Zool Res. 2023 Mar 18;44(2):315-322. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.399. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 36785898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis are resilient to intermittent fasting.EMBO Rep. 2023 Dec 6;24(12):e57268. doi: 10.15252/embr.202357268. Epub 2023 Nov 21. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37987220 Free PMC article.
-
Single Prolonged Stress Decreases the Level of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in C57BL/6, but Not in House Mice.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 6;45(1):524-537. doi: 10.3390/cimb45010035. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36661521 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal deletion of phosphatase and tensin homolog in mice results in spatial dysregulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Dec 7;16:1308066. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1308066. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38130682 Free PMC article.
-
Evidences for Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Humans.J Neurosci. 2021 Mar 24;41(12):2541-2553. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0675-20.2020. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33762406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predation drives the evolution of brain cell proliferation and brain allometry in male Trinidadian killifish, Rivulus hartii.Proc Biol Sci. 2019 Dec 18;286(1917):20191485. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.1485. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Proc Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31822257 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

