Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer?
- PMID: 29308325
- PMCID: PMC5749653
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1393134
Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer?
Abstract
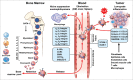
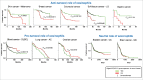
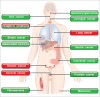
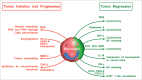
Prolonged low-grade inflammation or smoldering inflammation is a hallmark of a cancer. Eosinophils are components of the immune microenvironment that modulates tumor initiation and progression. Although canonically associated with a detrimental role in allergic disorders, these cells can induce a protective immune response against helminthes, viral and bacterial pathogens. Eosinophils are a source of anti-tumorigenic (e.g., TNF-α, granzyme, cationic proteins, and IL-18) and protumorigenic molecules (e.g., pro-angiogenic factors) depending on the milieu. In several neoplasias (e.g., melanoma, gastric, colorectal, oral and prostate cancer) eosinophils play an anti-tumorigenic role, in others (e.g., Hodgkin's lymphoma, cervical carcinoma) have been linked to poor prognosis, whereas in yet others they are apparently innocent bystanders. These seemingly conflicting results suggest that the role of eosinophils and their mediators could be cancer-dependent. The microlocalization (e.g., peritumoral vs intratumoral) of eosinophils could be another important aspect in the initiation/progression of solid and hematological tumors. Increasing evidence in experimental models indicates that activation/recruitment of eosinophils could represent a new therapeutic strategy for certain tumors (e.g., melanoma). Many unanswered questions should be addressed before we understand whether eosinophils are an ally, adversary or neutral bystanders in different types of human cancers.
Keywords: angiogenesis; cancer; eosinophils; inflammation; melanoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Mast Cells MASTers in Cancer?Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 12;8:424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00424. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28446910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basophils in Tumor Microenvironment and Surroundings.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1224:21-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-35723-8_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32036602 Review.
-
Controversial role of mast cells in skin cancers.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Jan;26(1):11-17. doi: 10.1111/exd.13107. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27305467
-
Eosinophils in Cancer: Favourable or Unfavourable?Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(7):650-66. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160119094313. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26785997 Review.
-
Expression and production of the CXC chemokine growth-related oncogene-alpha by human eosinophils.J Immunol. 2003 May 15;170(10):5309-16. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.10.5309. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12734381
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic inflammation promotes CCL6-dependent metastatic tumor growth.Sci Adv. 2021 May 26;7(22):eabb5943. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5943. Print 2021 May. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34039594 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral immune biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibition of solid tumours.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Aug;14(8):e1814. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1814. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39162097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pleiotropic Immunomodulatory Functions of IL-33 and Its Implications in Tumor Immunity.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2601. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02601. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30483263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The percentage of peripheral eosinophils as a sensitive marker for differentiating FIGO grade in endometrial adenocarcinomas.J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2022 Jun 1;23(2):99-105. doi: 10.4274/jtgga.galenos.2022.2021-9-10. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35263838 Free PMC article.
-
Successful management of severe bronchial asthma exacerbated by anti-PD-L1 treatment: A report of two cases.Respirol Case Rep. 2021 Oct 24;9(11):e0868. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.868. eCollection 2021 Nov. Respirol Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34721879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kay AB. The early history of the eosinophil. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015;45(3):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.12480. PMID:25544991 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Johnston LK, Bryce PJ. Understanding Interleukin 33 and Its Roles in Eosinophil Development. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017;4(51); https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Varricchi G, Bagnasco D, Borriello F, Heffler E, Canonica GW. Interleukin-5 pathway inhibition in the treatment of eosinophilic respiratory disorders: evidence and unmet needs. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;16(2):186–200; https://doi.org/10.1097/aci.0000000000000251. PMID:26859368 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg HF, Dyer KD, Foster PS. Eosinophils: changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(1):9–22; https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3341. PMID:23154224 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Atkins FD, Lee NA, Lee JJ. Changing roles of eosinophils in health and disease. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;113(1):3–8; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2014.04.002. PMID:24795292 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
