Extracellular matrix molecules and their potential contribution to the function of transplanted pancreatic islets
- PMID: 29306997
- PMCID: PMC6449002
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4524-8
Extracellular matrix molecules and their potential contribution to the function of transplanted pancreatic islets
Abstract
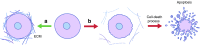
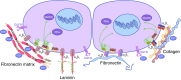
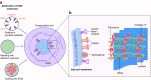
Extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules are responsible for structural and biochemical support, as well as for regulation of molecular signalling and tissue repair in many organ structures, including the pancreas. In pancreatic islets, collagen type IV and VI, and laminins are the most abundant molecules, but other ECM molecules are also present. The ECM interacts with specific combinations of integrin α/β heterodimers on islet cells and guides many cellular processes. More specifically, some ECM molecules are involved in beta cell survival, function and insulin production, while others can fine tune the susceptibility of islet cells to cytokines. Further, some ECM induce release of growth factors to facilitate tissue repair. During enzymatic isolation of islets for transplantation, the ECM is damaged, impacting islet function. However, restoration of the ECM in human islets (for example by adding ECM to the interior of immunoprotective capsules) has been shown to enhance islet function. Here, we provide current insight into the role of ECM molecules in islet function and discuss the clinical potential of ECM manipulation to enhance pancreatic islet function and survival.
Keywords: Collagen; Cytokines; Extracellular matrix; Graft; Islet; Laminin; Review.
Conflict of interest statement
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Contribution statement
All authors were responsible for drafting and revising this article and approved the version to be published.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular matrix inclusion in immunoisolating alginate-based microcapsules promotes longevity, reduces fibrosis, and supports function of islet allografts in vivo.Acta Biomater. 2023 Mar 1;158:151-162. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.12.068. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36610609
-
Inclusion of extracellular matrix molecules and necrostatin-1 in the intracapsular environment of alginate-based microcapsules synergistically protects pancreatic β cells against cytokine-induced inflammatory stress.Acta Biomater. 2022 Jul 1;146:434-449. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.04.042. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35500812
-
Laminin and collagen IV inclusion in immunoisolating microcapsules reduces cytokine-mediated cell death in human pancreatic islets.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018 Feb;12(2):460-467. doi: 10.1002/term.2472. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018. PMID: 28508555
-
Therapeutic Strategies for Modulating the Extracellular Matrix to Improve Pancreatic Islet Function and Survival After Transplantation.Curr Diab Rep. 2018 May 19;18(7):39. doi: 10.1007/s11892-018-1014-4. Curr Diab Rep. 2018. PMID: 29779190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix in pancreatic islets: relevance to scaffold design and transplantation.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(1):1-12. doi: 10.3727/096368909788237195. Cell Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19476204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stem Cell Therapy for the Management of Type 1 Diabetes: Advances and Perspectives.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(5):549-561. doi: 10.2174/0118715303256582230919093535. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37861029 Review.
-
Functionalized Collagen/Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Interpenetrating Network Hydrogel Enhances Beta Pancreatic Cell Sustenance.Gels. 2023 Jun 19;9(6):496. doi: 10.3390/gels9060496. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37367166 Free PMC article.
-
3D evaluation of the extracellular matrix of hypoxic pancreatic islets using light sheet fluorescence microscopy.Islets. 2024 Dec 31;16(1):2298518. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2023.2298518. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Islets. 2024. PMID: 38267218 Free PMC article.
-
Host Subcellular Organelles: Targets of Viral Manipulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 29;25(3):1638. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031638. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix and the maintenance and loss of peripheral immune tolerance in autoimmune insulitis.Curr Opin Immunol. 2018 Dec;55:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30248522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

