CD34+ Cell Selection versus Reduced-Intensity Conditioning and Unmodified Grafts for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Patients Age >50 Years with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- PMID: 29305194
- PMCID: PMC6800017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.12.804
CD34+ Cell Selection versus Reduced-Intensity Conditioning and Unmodified Grafts for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Patients Age >50 Years with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Abstract
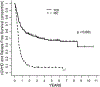
Reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) and T cell depletion (TCD) through CD34+ cell selection without the use of post-transplantation immunosuppression are 2 strategies used to reduce nonrelapse mortality (NRM) in older patients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). To compare the efficacy of the RIC and TCD approaches, we evaluated the outcomes of patients age >50 years with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) who underwent allo-HCT from an HLA-matched donor with one of these strategies. Baseline characteristics were comparable in the patients receiving TCD (n = 204) and those receiving RIC (n = 151), except for a higher proportion of unrelated donors (68% versus 40%; P < .001) and a higher comorbidity burden (Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index [HCT-CI] ≥3: 51% versus 38%; P < .001) in the TCD cohort. Analysis of outcomes at 3 years showed a higher chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)/relapse-free survival (CRFS) (51% versus 7%; P < .001), lower incidences of grade II-IV acute GVHD (18% versus 46% at day +180) and chronic GVHD (6% versus 55% at 3 years; P < .001), and a lower incidence of relapse (19% versus 33% at 3 years; P = .001) in the TCD group compared with the RIC group. Relapse-free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS), and NRM were similar in the 2 groups. Combining transplantation approach (RIC versus TCD) and comorbidity burden (HCT-CI 0-2 versus ≥3), patients with an HCT-CI score of 0-2 seemed to benefit from the TCD approach. In conclusion, in this retrospective study, the use of a CD34+ cell-selected graft and a myeloablative conditioning regimen was associated with higher CRFS and similar RFS and OS compared with unmodified allo-RIC in patients age >50 years with AML and MDS.
Keywords: Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation; GVHD; RIC; T cell depletion.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
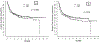
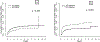
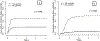
Similar articles
-
The Dilemma of Conditioning Intensity: When Does Myeloablative Conditioning Improve Outcomes for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Mar;25(3):606-612. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30244109
-
Busulfan dose intensity and outcomes in reduced-intensity allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid leukemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013 Jun;19(6):981-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.03.016. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23562738
-
Impact of spliceosome mutation on outcomes of myelodysplastic syndrome and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Leuk Res. 2024 Oct;145:107565. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2024.107565. Epub 2024 Aug 25. Leuk Res. 2024. PMID: 39208597
-
Comparison of reduced-intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Nov 1;23(21):2535-52. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0123. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 25072307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute graft-versus-host disease.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023 Jun 8;9(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00438-1. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023. PMID: 37291149 Review.
-
Ex vivo and in vivo T cell-depleted allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission resulted in similar overall survival: on behalf of the ALWP of the EBMT and the MSKCC.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Oct 20;11(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0668-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30342553 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase II Multicenter Study of the Addition of Azacitidine to Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Allogeneic Transplant for High-Risk Myelodysplasia (and Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia): Results of CALGB 100801 (Alliance).Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Oct;25(10):1984-1992. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Jun 15. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31212080 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation with CD34+ Cell Selection.Clin Hematol Int. 2019 Sep 1;1(3):154-160. doi: 10.2991/chi.d.190613.001. eCollection 2019 Sep. Clin Hematol Int. 2019. PMID: 34595425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Ex Vivo T Cell Depletion - Where Do We Stand?Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2019 Jan;2(1):e29. doi: 10.1002/acg2.29. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31106295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martino R, Iacobelli S, Brand R, et al. Retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using HLA-identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2006;108(3):836–846. - PubMed
-
- Valcárcel D, Martino R, Caballero D, et al. Sustained remissions of high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome after reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation: chronic graft-versus-host disease is the strongest factor improving survival. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(4):577–584. - PubMed
-
- Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, et al. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2010;116(22):4439–4443. - PubMed
-
- Martino R, Henseler A, van Lint M, et al. Long-term follow-up of a retrospective comparison of reduced-intensity conditioning and conventional high-dose conditioning for allogeneic transplantation from matched related donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

