HDAC inhibition as a treatment concept to combat temsirolimus-resistant bladder cancer cells
- PMID: 29299126
- PMCID: PMC5746361
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.22454
HDAC inhibition as a treatment concept to combat temsirolimus-resistant bladder cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Although the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) might be a promising molecular target to treat advanced bladder cancer, resistance develops under chronic exposure to an mTOR inhibitor (everolimus, temsirolimus). Based on earlier studies, we proposed that histone deacetylase (HDAC) blockade might circumvent resistance and investigated whether HDAC inhibition has an impact on growth of bladder cancer cells with acquired resistance towards temsirolimus.
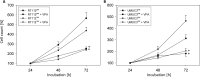
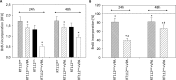
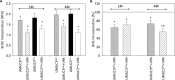
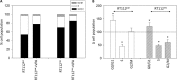
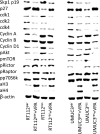
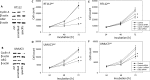
Results: The HDAC inhibitor valproic acid (VPA) significantly inhibited growth, proliferation and caused G0/G1 phase arrest in RT112res and UMUC-3res. cdk1, cyclin B, cdk2, cyclin A and Skp1 p19 were down-regulated, p27 was elevated. Akt-mTOR signaling was deactivated, whereas acetylation of histone H3 and H4 in RT112res and UMUC-3res increased in the presence of VPA. Knocking down cdk2 or cyclin A resulted in a significant growth blockade of RT112res and UMUC-3res.
Materials and methods: Parental (par) and resistant (res) RT112 and UMUC-3 cells were exposed to the HDAC inhibitor VPA. Tumor cell growth, proliferation, cell cycling and expression of cell cycle regulating proteins were then evaluated. siRNA blockade was used to investigate the functional impact of the proteins.
Conclusions: HDAC inhibition induced a strong response of temsirolimus-resistant bladder cancer cells. Therefore, the temsirolimus-VPA-combination might be an innovative strategy for bladder cancer treatment.
Keywords: HDAC inhibition; bladder cancer; temsirolimus-resistance; tumor growth; valproic acid (VPA).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic Sulforaphane Administration Inhibits Resistance to the mTOR-Inhibitor Everolimus in Bladder Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 4;21(11):4026. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114026. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512849 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC Inhibition Counteracts Metastatic Re-Activation of Prostate Cancer Cells Induced by Chronic mTOR Suppression.Cells. 2018 Sep 1;7(9):129. doi: 10.3390/cells7090129. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30200497 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the HDAC Inhibitor Valproic Acid on the Growth and Proliferation of Temsirolimus-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 19;11(4):566. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040566. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31010254 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC inhibition delays cell cycle progression of human bladder cancer cells in vitro.Anticancer Drugs. 2011 Nov;22(10):1002-9. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32834a2c70. Anticancer Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21822119
-
mTOR inhibitors in urinary bladder cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11541-11551. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5083-1. Epub 2016 May 27. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27235118 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy in Bladder Cancer: Current Methods and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 7;12(5):1181. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051181. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32392774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Sulforaphane Administration Inhibits Resistance to the mTOR-Inhibitor Everolimus in Bladder Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 4;21(11):4026. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114026. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32512849 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder Cancer Metastasis Induced by Chronic Everolimus Application Can Be Counteracted by Sulforaphane In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 4;21(15):5582. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155582. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32759798 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Mitochondrial Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 in Urological Cancers From the Perspective of Ferroptosis and Cellular Senescence.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 20;10:850145. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.850145. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35517510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC Inhibition Counteracts Metastatic Re-Activation of Prostate Cancer Cells Induced by Chronic mTOR Suppression.Cells. 2018 Sep 1;7(9):129. doi: 10.3390/cells7090129. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30200497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2016.
-
- Morales-Barrera R, Suárez C, de Castro AM, Racca F, Valverde C, Maldonado X, Bastaros JM, Morote J, Carles J. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors and immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of advanced bladder cancer: New direction and New Hope. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;50:208–216. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

