Macrophages orchestrate breast cancer early dissemination and metastasis
- PMID: 29295986
- PMCID: PMC5750231
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02481-5
Macrophages orchestrate breast cancer early dissemination and metastasis
Abstract
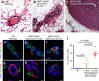
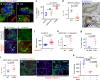
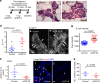
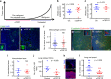
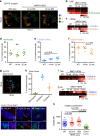
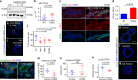
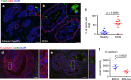
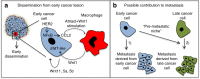
Cancer cell dissemination during very early stages of breast cancer proceeds through poorly understood mechanisms. Here we show, in a mouse model of HER2+ breast cancer, that a previously described sub-population of early-evolved cancer cells requires macrophages for early dissemination. Depletion of macrophages specifically during pre-malignant stages reduces early dissemination and also results in reduced metastatic burden at end stages of cancer progression. Mechanistically, we show that, in pre-malignant lesions, CCL2 produced by cancer cells and myeloid cells attracts CD206+/Tie2+ macrophages and induces Wnt-1 upregulation that in turn downregulates E-cadherin junctions in the HER2+ early cancer cells. We also observe macrophage-containing tumor microenvironments of metastasis structures in the pre-malignant lesions that can operate as portals for intravasation. These data support a causal role for macrophages in early dissemination that affects long-term metastasis development much later in cancer progression. A pilot analysis on human specimens revealed intra-epithelial macrophages and loss of E-cadherin junctions in ductal carcinoma in situ, supporting a potential clinical relevance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CYP4A in tumor-associated macrophages promotes pre-metastatic niche formation and metastasis.Oncogene. 2017 Aug 31;36(35):5045-5057. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.118. Epub 2017 May 8. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28481877 Free PMC article.
-
VDR status arbitrates the prometastatic effects of tumor-associated macrophages.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Aug;12(8):1181-91. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0036. Epub 2014 May 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24821711
-
Follistatin is a metastasis suppressor in a mouse model of HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 5;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0857-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28583174 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis tumor antigen family proteins during breast cancer progression and metastasis in a reliable mouse model for human breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;12(5):1479-86. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1519. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16533771
-
HOXB7 promotes malignant progression by activating the TGFβ signaling pathway.Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;75(4):709-19. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3100. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25542862 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phase-Transformation Nanoparticle-Mediated Sonodynamic Therapy: An Effective Modality to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Response by Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death in Breast Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 5;16:1913-1926. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S297933. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33707946 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding tissue-resident macrophages unlocks the potential for novel combinatorial strategies in breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1375528. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375528. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39104525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZFP281 drives a mesenchymal-like dormancy program in early disseminated breast cancer cells that prevents metastatic outgrowth in the lung.Nat Cancer. 2022 Oct;3(10):1165-1180. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00424-8. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Nat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36050483
-
Comprehensive characterization of early-programmed tumor microenvironment by tumor-associated macrophages reveals galectin-1 as an immune modulatory target in breast cancer.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 1;14(2):843-860. doi: 10.7150/thno.88917. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38169569 Free PMC article.
-
Microenvironmental modulation of the developing tumour: an immune-stromal dialogue.Mol Oncol. 2021 Oct;15(10):2600-2633. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12773. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Mol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32741067 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

