A Computational-Based Approach to Identify Estrogen Receptor α/ β Heterodimer Selective Ligands
- PMID: 29295894
- PMCID: PMC5801554
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.117.108696
A Computational-Based Approach to Identify Estrogen Receptor α/ β Heterodimer Selective Ligands
Abstract
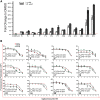
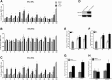
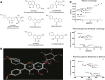
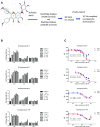
The biologic effects of estrogens are transduced by two estrogen receptors (ERs), ERα and ERβ, which function in dimer forms. The ERα/α homodimer promotes and the ERβ/β inhibits estrogen-dependent growth of mammary epithelial cells; the functions of ERα/β heterodimers remain elusive. Using compounds that promote ERα/β heterodimerization, we have previously shown that ERα/β heterodimers appeared to inhibit tumor cell growth and migration in vitro. Further dissection of ERα/β heterodimer functions was hampered by the lack of ERα/β heterodimer-specific ligands. Herein, we report a multistep workflow to identify the selective ERα/β heterodimer-inducing compound. Phytoestrogenic compounds were first screened for ER transcriptional activity using reporter assays and ER dimerization preference using a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assay. The top hits were subjected to in silico modeling to identify the pharmacophore that confers ERα/β heterodimer specificity. The pharmacophore encompassing seven features that are potentially important for the formation of the ERα/β heterodimer was retrieved and subsequently used for virtual screening of large chemical libraries. Four chemical compounds were identified that selectively induce ERα/β heterodimers over their respective homodimers. Such ligands will become unique tools to reveal the functional insights of ERα/β heterodimers.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 2;105(48):19012-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807274105. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19022902 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of estrogen receptor dimer selective ligands reveals growth-inhibitory effects on cells that co-express ERα and ERβ.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030993. Epub 2012 Feb 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347418 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor mediated biological activities of phytoestrogens.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Oct;278(Pt 2):134320. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134320. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39084415
-
Selectively targeting estrogen receptors for cancer treatment.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Oct 30;62(13):1265-76. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.08.001. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 20708050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen signaling: a subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta.Mol Interv. 2003 Aug;3(5):281-92. doi: 10.1124/mi.3.5.281. Mol Interv. 2003. PMID: 14993442 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Role of Estrogen Receptor β in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;12(6):1477. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061477. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32516978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERpred: a web server for the prediction of subtype-specific estrogen receptor antagonists.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 9;9:e11716. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11716. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34285834 Free PMC article.
-
Cosmosiin Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting PD-L1 Expression and Inducing ROS.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 18;12(12):2131. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122131. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136250 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule conjugates with selective estrogen receptor β agonism promote anti-aging benefits in metabolism and skin recovery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 May;14(5):2137-2152. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.01.014. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38799642 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-Aided Ligand Discovery for Estrogen Receptor Alpha.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 12;21(12):4193. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124193. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32545494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anstead GM, Carlson KE, Katzenellenbogen JA. (1997) The estradiol pharmacophore: ligand structure-estrogen receptor binding affinity relationships and a model for the receptor binding site. Steroids 62:268–303. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski AM, Pike AC, Dauter Z, Hubbard RE, Bonn T, Engström O, Ohman L, Greene GL, Gustafsson JA, Carlquist M. (1997) Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 389:753–758. - PubMed
-
- Caballero J. (2010) 3D-QSAR (CoMFA and CoMSIA) and pharmacophore (GALAHAD) studies on the differential inhibition of aldose reductase by flavonoid compounds. J Mol Graph Model 29:363–371. - PubMed
-
- Cowley SM, Hoare S, Mosselman S, Parker MG. (1997) Estrogen receptors α and β form heterodimers on DNA. J Biol Chem 272:19858–19862. - PubMed
-
- Grober OMV, Mutarelli M, Giurato G, Ravo M, Cicatiello L, De Filippo MR, Ferraro L, Nassa G, Papa MF, Paris O, et al. (2011) Global analysis of estrogen receptor beta binding to breast cancer cell genome reveals an extensive interplay with estrogen receptor alpha for target gene regulation. BMC Genomics 12:36. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
