A cell-penetrating whole molecule antibody targeting intracellular HBx suppresses hepatitis B virus via TRIM21-dependent pathway
- PMID: 29290826
- PMCID: PMC5743566
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.20047
A cell-penetrating whole molecule antibody targeting intracellular HBx suppresses hepatitis B virus via TRIM21-dependent pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum: A cell-penetrating whole molecule antibody targeting intracellular HBx suppresses hepatitis B virus via TRIM21-dependent pathway: Erratum.Theranostics. 2022 Apr 26;12(8):3601. doi: 10.7150/thno.72666. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35664069 Free PMC article.
Abstract
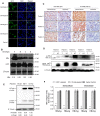
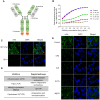
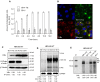
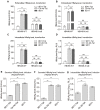
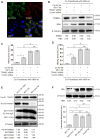
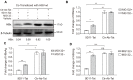
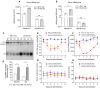
Rationale: Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) mostly targeting extracellular or cell surface molecules have been widely used in the treatment of various diseases. However, mAbs cannot pass through the cell membrane as efficiently as small compounds, thus limiting their use against intracellular targets. Methods to shuttle antibodies into living cells may largely expand research and application in areas based on mAbs. Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) is an important intracellular multi-functional viral protein in the life cycle of hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBx plays essential roles in virus infection and replication and is strongly associated with HBV-related carcinogenesis. Methods: In this study, we developed a cell-penetrating whole molecule antibody targeting HBx (9D11-Tat) by the fusion of a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) on the C-terminus of the heavy chain of a potent mAb specific to HBx (9D11). The anti-HBV effect and mechanism of 9D11-Tat were investigated in cell and mouse models mimicking chronic HBV infection. Results: Our results demonstrated that the recombinant 9D11-Tat antibody could efficiently internalize into living cells and significantly suppress viral transcription, replication, and protein production both in vitro and in vivo. Further analyses suggested the internalized 9D11-Tat antibody could greatly reduce intracellular HBx via Fc binding receptor TRIM21-mediated protein degradation. This process simultaneously stimulated the activations of NF-κB, AP-1, and IFN-β, which promoted an antiviral state of the host cell. Conclusion: In summary, our study offers a new approach to target intracellular pathogenesis-related protein by engineered cell-penetrating mAb expanding their potential for therapeutic applications. Moreover, the 9D11-Tat antibody may provide a novel therapeutic agent against human chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus X protein; antibodies for intracellular targets; antibody-mediated intracellular immunity; cell-penetrating peptide; hepatitis B virus.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 restricts hepatitis B virus replication by targeting HBx for proteasomal degradation.Antiviral Res. 2021 Aug;192:105107. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105107. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Antiviral Res. 2021. PMID: 34097931
-
Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBx.J Hepatol. 2021 Mar;74(3):522-534. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.019. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 32987030
-
Anti-HBV drugs suppress the growth of HBV-related hepatoma cells via down-regulation of hepatitis B virus X protein.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28192212
-
Developments in Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Antiviral Agents and as Vehicles for Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acid Targeting Hepadnaviral Replication Pathway.Biomolecules. 2018 Jul 16;8(3):55. doi: 10.3390/biom8030055. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30013006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cell Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) and Cationic Polymers for Chronic Hepatitis B.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 27;16(12):28230-41. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226094. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26633356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Avoiding the self-nucleation interference: a pH-regulated gold in situ growth strategy to enable ultrasensitive immunochromatographic diagnostics.Theranostics. 2022 Mar 14;12(6):2801-2810. doi: 10.7150/thno.70092. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35401815 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM21 Aggravates Herpes Simplex Virus Epithelial Keratitis by Attenuating STING-IRF3-Mediated Type I Interferon Signaling.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 16;11:703. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00703. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32373102 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol consumption and HBV induce abnormal lipid metabolism through HBx/SWELL1/arachidonic acid signaling and activate Tregs in HBV-Tg mice.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 23;10(20):9249-9267. doi: 10.7150/thno.46005. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32802190 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA as novel technology for passive immunotherapy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jan;76(2):301-328. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2935-4. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30334070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B x antigen (HBx) is an important therapeutic target in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2021 Nov 23;12(24):2421-2433. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28077. eCollection 2021 Nov 23. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34853663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leavy O. Therapeutic antibodies: past, present and future. Nature reviews Immunology. 2010;10:297. - PubMed
-
- Gura T. Therapeutic antibodies: magic bullets hit the target. Nature. 2002;417:584–6. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser PD, Maier J, Traenkle B, Emele F, Rothbauer U. Recent progress in generating intracellular functional antibody fragments to target and trace cellular components in living cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1844:1933–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

